Insulated Bearings Buyer’s Guide
Introduction
Insulated bearings have become an indispensable part of many mechanical devices in today’s highly electrified industrial environment. They cannot only effectively isolate the current and prevent the occurrence of electrical faults but also maintain stable performance under extreme working conditions to ensure the long-term, reliable operation of the equipment. However, in the face of a wide range of insulated bearings on the market, making a wise choice has become a complex problem for many purchasers and engineers. This buyer’s guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive and practical reference for the selection of insulated bearings. Through a deeper understanding of the working principle, performance characteristics, and application scenarios of insulation bearings, you can evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different products more accurately and find the most suitable insulation bearings for your needs.
Definition of Insulated Bearings
Insulated bearings are a general term for a class of bearings that can block the passage of electric current and have insulating properties in the bearing itself. These properties are usually realized through special processes, such as in the bearing outer ring or inner ring coated with a layer of insulating material or its rolling body made of ceramic and other insulating materials. The name and code of insulated bearings follow the international bearing code standard.
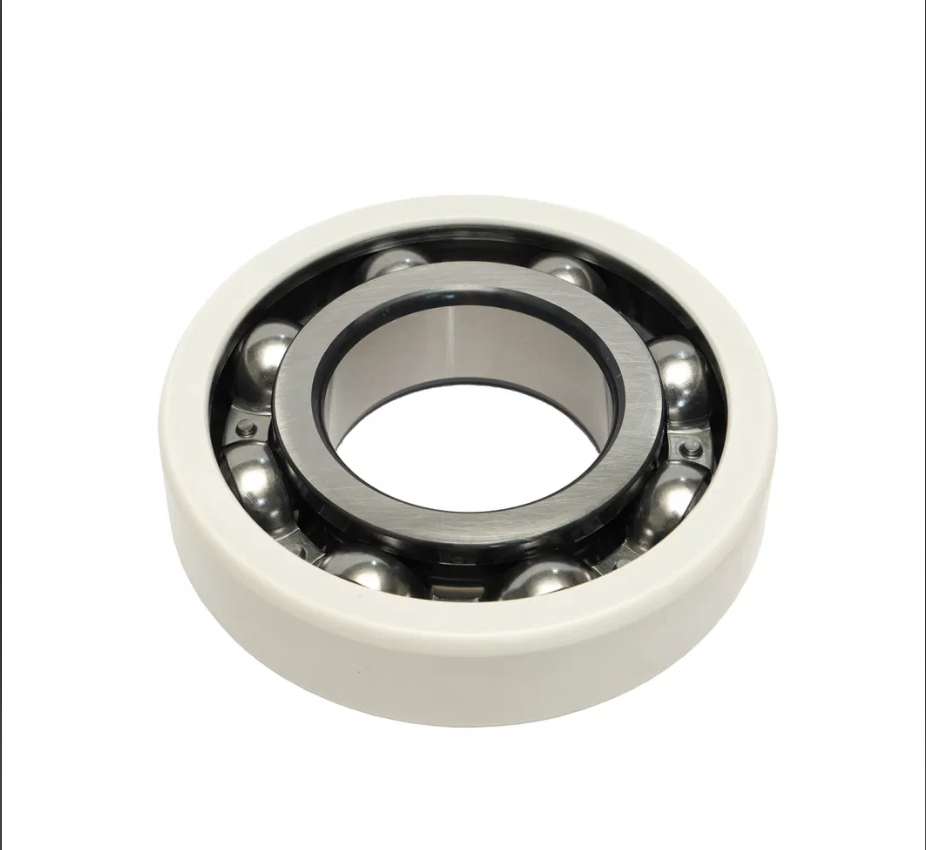

Principle of operation of insulated bearings
The primary technical characteristics of insulated bearings are similar to those of ordinary bearings, which consist of a steel inner ring, an outer ring, a set of keepers (such as a steel stamping cage or brass solid cage, etc.) and a set of steel balls (or rollers). But to give its insulating properties, it will be in a specific part of the bearing (such as the inner ring or outer ring) using a plasma spraying process spraying a layer of insulating coatings, such as alumina, silicon nitride coating, or rolling body using ceramic materials. These insulating coatings or materials can cut off the current circuit and prevent the current from damaging the bearings, grease, rolling elements and raceways, thus increasing the service life of the bearings.
Types of insulating materials
The main types of insulating materials for insulated bearings include the following:
I: Ceramic Coating
Features: Insulated bearings often use ceramic coatings as insulating materials. These coatings usually have high hardness, wear resistance, good thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical insulation properties. Common ceramic oxide materials such as alumina are used to make these coatings.
Process: The ceramic coating is uniformly applied to the surface of the outer or inner ring of the bearing by advanced processes such as plasma spraying. The thickness of the coating is generally between 50~200μm, some even up to 0.2mm~0.4mm, to ensure sufficient insulation strength and wear resistance.
II: Special PPS coating
Features: PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) is a polymer with excellent insulating properties. Special coatings with higher insulation resistance and breakdown voltage can be produced by improving the formulation and process of PPS materials.
Application: Special PPS coatings can also be applied to bearings’ outer or inner ring surfaces to form a dense insulating layer, which is suitable for applications requiring stable electrical insulation properties in harsh environments.
III: Ceramic Roller
Features: In addition to coated insulation, there is another type of insulated bearing with rolling elements made of ceramic materials (e.g., silicon nitride). The ceramic rolling body has a very high resistivity, making it difficult for current to pass through it, thus realizing the bearing’s electrical insulation.
Advantage: Ceramic rolling element insulated bearings not only have good electrical insulation properties but also have the advantages of high strength, wear resistance and high-temperature resistance, which makes them suitable for high speed, high temperature, high humidity and other harsh environments, such as motors and other equipment.
Areas of application for insulated bearings
Insulated bearings are often used in equipment prone to undergo electrical currents that produce galvanic damage, mainly in the power industry, railroad facilities, medical equipment and metallurgical industry, mining machinery industry, and petrochemical industry. With the advent of the Industry 4.0 era, insulated bearings will be utilized in the new energy industry, as well as intelligent robots and semiconductor equipment.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insulated Bearings
The main factors to be considered when selecting insulated bearings include insulation properties, size and accuracy, load-carrying capacity and life, environmental conditions and cost budget.
Load capacity and performance requirements
I: Load capacity:
Size and nature of load: The selection of insulated bearings should be based on the size and nature of the load. For example, when the load is light and smooth, it is appropriate to choose ball bearings; and when the load is large and shock, it is appropriate to choose roller bearings.
Load direction: when the bearing bears pure radial load, deep groove ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings or needle roller bearings; when bearing pure axial load, thrust ball bearings should be used; when at the same time bearing radial and axial load, you can choose angular contact ball bearings or tapered roller bearings.
II: Performance requirements:
Speed: Because the rolling resistance of ball bearings is smaller, under the same size and precision, the limiting speed of ball bearings is higher than that of roller bearings, so ball bearings should be preferred at high speed.
Centring performance: when the shaft span is large, bending stiffness is small or due to processing and installation reasons caused by the shaft ends of the bearing having a large different centre, it should be used with an automatic centring performance of self-aligning spherical ball bearings or spherical roller bearings.
Insulation performance: insulated bearings use a special spraying process. The outer ring or inner ring surface has a layer of uniform thickness, and strong adhesion coating, and can withstand up to 1000 V DC voltage, to avoid induced current on the bearings of the galvanic corrosion effect, to prevent the current on the lubricating grease and rolling body, raceway caused by damage to improve the service life of the bearings.
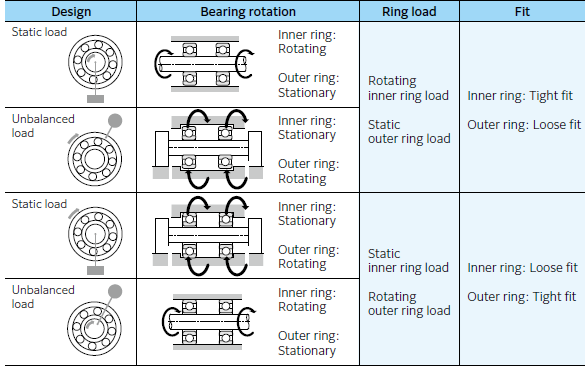
Impact of environmental conditions
The main environmental conditions to be considered when selecting insulated bearings include the following:
- Electromagnetic environment: The main function of insulated bearings is to prevent the galvanic corrosion effect of induced currents on bearings and to avoid the damage caused by the current to the grease and rolling body and raceway. Therefore, insulated bearings, such as motors, generators, and other equipment, are particularly important in the complex electromagnetic environment.
- Humidity and Temperature: Coatings for insulated bearings need to be able to withstand certain humidity and temperature variations. A special spraying process creates a coating of uniform thickness with excellent adhesion, making it unaffected by moisture and humidity.
- Corrosive environment: in some corrosive environments, such as strong acid and alkali liquids, ordinary stainless steel bearings may not be able to completely prevent rust, which requires the selection of insulated bearings with better anti-rust properties.
- High-temperature environment: In high-temperature environments, insulated bearings require special treatment to ensure that their performance is not affected. Usually, it is necessary to inquire about the use temperature and limit temperature in advance to prevent the bearings’ service life from being affected by the high working temperature.
Cost and budget considerations
Cost budgeting is an important consideration when selecting insulated bearings. The cost of insulated bearings is mainly influenced by the following factors:
- Material cost: Insulated bearings usually use a special spraying process to spray a high-quality coating on the outer surface of the bearing, and the choice of coating material will affect the cost. Ceramic coatings and special PPS coatings have their own unique advantages, but costs can vary.
- Process Costs: Specialized spray processes and coating treatments add to the cost of production, and the complexity and technical requirements of these processes affect the final cost.
- Brand and quality control: the price of different brands of insulated bearings varies considerably. Well-known brands usually offer better quality and performance guarantees, but they are also relatively expensive.
- Application scenarios: The application scenarios for insulated bearings also affect the cost. For example, insulated bearings used in harsh environments such as high speeds, high temperatures, and high humidity will cost more due to their special design and material selection.
- Maintenance and Replacement Costs: While the initial investment in insulated bearings may be high, their long-term stable operation reduces maintenance and replacement costs due to galvanic current erosion.
Dimensions and Accuracy
Size Requirements:
- Inner Diameter, Outer Diameter and Width: Insulated bearings are available in inner diameters ranging from 40mm to 140mm, outer diameters ranging from 80mm to 300mm, and widths ranging from 18mm to 62mm.1 These dimensions need to be matched to the design requirements of the machinery and equipment to ensure that the bearings can be mounted without problems and that they have sufficient space to cope with thermal expansion and contraction.
- Radial cross-section height: If the radial space of the bearing mounting part is limited, the bearings with smaller radial cross-section height should be used preferentially, such as angular contact ball bearings and deep groove ball bearings.
Accuracy Requirements:
- Precision grade: For high-precision mechanical equipment, such as machine tool spindles and precision instruments, higher precision bearings should be selected. For example, P5 and P4 grade bearings are suitable for high-precision machine tools and grinding machines, while the aerospace field requires the selection of ultra-precision bearings with P2 grade.
- Tolerance grade: The tolerance grade of the bearing directly affects its rotational accuracy and the performance of mechanical equipment. For high precision requirements of mechanical equipment, should choose higher tolerance grade bearings, such as deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, tapered roller bearings and thrust angular contact ball bearings.
Various tests on insulated bearings
The following aspects need to be tested when selecting insulated bearings, through which the performance of insulated bearings can be comprehensively assessed to ensure their reliability and durability under various working conditions.

Insulation resistance measurement
In order to guarantee the insulation performance, it is necessary to measure the insulation of the insulated bearings, including the insulation resistance of the bearings, the shaft voltage and the shaft current. The bearing can be mounted on the rotating shaft, and an insulation resistance meter of 250V specification can be used for the measurement. The specific operation is to connect the E end of the meter to the rotating shaft, and the insulating part of the bearing (e.g. the outer ring) is covered with aluminium foil and then fixed with a bare copper wire tie and connected to the L end of the meter. Alternatively, the insulated bearing is mounted in the bearing chamber of the housing or motor end cap, and the insulation resistance between the shaft and the housing or motor end cap is measured in a state where there is no electrical access between the housing or motor end cap and the rotor shaft on which the insulated bearing is mounted.
Shaft voltage and shaft current testing
Insulation rings are added between the motor bearings, and the housing (dry insulating sheets are padded between the bearings and the rotating shaft), or insulated bearings are used to ensure that the motor bearings are well insulated. For the first measurement, the motor under test should be run at rated voltage and rated frequency with no load, and the shaft voltage should be measured with a high internal resistance millivoltmeter with a range of 100mV. Then, short one end of the rotating shaft to the ground and measure the shaft voltage from the other bearing seat to the ground. For the second measurement, the motor under test is loaded with rated load running at rated current and rated frequency, and the bearing voltage is measured.
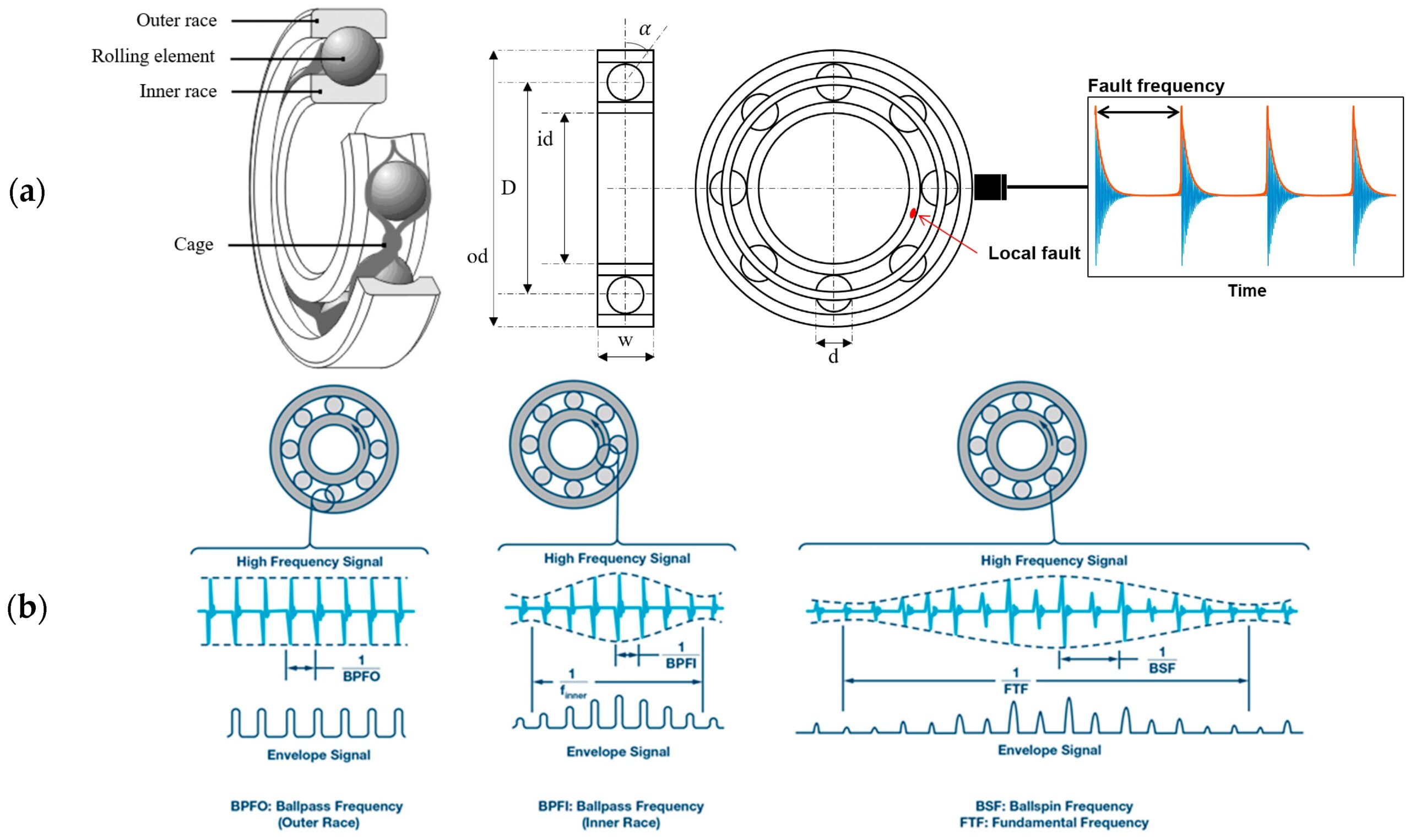
Vibration Detection
Bearing testing also includes vibration testing, mainly through the vibration acceleration and vibration speed to determine the quality level of bearings. The vibration acceleration standard is divided into Z1, Z2, and Z3 three levels, while the vibration speed standard is divided into V, V1, V2, V3, and V4 five levels. Vibration testing can help to analyze whether the bearing has geometric dimension problems, quality problems of raceway/rolling body, quality problems of the cage, etc.
Mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy
Mechanical properties: including bearing hardness, wear resistance, compressive strength and so on. These properties directly affect the service life and stability of the bearing. They can be tested by hardness tests, wear resistance tests and other methods.
Dimensional accuracy: Test the geometric dimensions of the bearings, such as inner and outer ring diameter, thickness, rolling element diameter, etc., to ensure that their accuracy meets the standard. Dimensional accuracy directly affects the assembly and use of bearings.
Corrosion resistance and noise level
Corrosion resistance: Test the performance of bearings in wet and corrosive environments to assess their rust and corrosion resistance.
Noise level: Detect the noise level generated by the bearing during operation and evaluate its adaptability to the working environment and noise control performance. Test the dynamic balance of bearings during rotation to ensure that they remain smooth during rotation and avoid vibration and noise caused by unbalance.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Insulated Bearings
Proper use of insulated bearings can extend the life of the bearings and equipment and improve efficiency. Normally, you can pay more attention to the following aspects: routine maintenance, common troubleshooting and so on.

Daily Maintenance Tips
Routine maintenance tips for insulated bearings include the following areas
- Regular cleaning: Wipe the bearing surface with a clean cloth to remove dust, oil and impurities. At the same time, pay attention to checking the condition of the seals; if damaged or ageing, replace them in time.
- Check sealing: Ensure that the bearings are well sealed to prevent lubricant leakage and effectively block the intrusion of dust and moisture. When installing, sealing rings or sealing plugs should be added.
- Lubrication management: choose high-quality lubricating oil or grease suitable for the bearing type and working conditions, and add or replace it according to the specified period. It is extremely important to ensure that the lubrication is adequate and appropriate.
- Avoid overloading and violent shocks: Avoid overloading and violent shocks during driving to minimize excessive wear on the bearings.
- Inspection and replacement of worn parts: Regularly check the wear and tear of the inner and outer rings and rolling elements of the bearings and replace them if necessary. Judge the wear condition by measuring the relevant dimensions and observing the state of rolling bodies and cages.
- Adjustment of bearing clearance: According to the specified value and use requirements, the appropriate bearing clearance is set by adjusting the tightness of the inner and outer rings to ensure that the bearings can operate normally.
- Balanced Load Distribution: Efforts are made to minimize load imbalance and transient shocks and prevent bearings overloading.
Common Failures and Their Causes
Common failures of insulated bearings and their causes include the following:
- Galvanic corrosion: The main function of insulated bearings is to prevent galvanic corrosion, but if the insulation is damaged or fails, galvanic corrosion may result, affecting the service life of the bearings. The causes of galvanic corrosion may include damage to insulation, excessive voltage or current.
- Improper assembly: in the assembly process, if the bearing outer ring and bearing hole or bearing inner ring and shaft are improper, or assembly bearing heating temperature control is not appropriate, it will lead to the bearing temperature rising, aggravating the wear and damage, and even holding phenomenon.
- Lubrication Problems: Inadequate lubrication or improper lubricant selection can lead to overheating and increased wear of bearings. If the grease is ageing, contaminated or leaking, it will also affect the bearing’s normal operation.
- Oil seal problem: Poor quality or dry friction of oil seals will lead to a sharp rise in bearing temperature, which in turn affects the bearings’ normal work.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting methods for insulated bearings include the following:
- Appearance inspection: Observe whether the inner and outer rings, rolling bodies, cages and other parts of the bearings have cracks, fragments, peeling, snagging, rust, indentation and other damage. If these conditions are found, it may indicate that the bearing has been damaged.
- Sound judgment: the use of a megaphone or listening stick on the bearing shell to listen to the sound of the bearing operation. Under normal circumstances, the bearing should issue a uniform and continuous “clatter” sound or lower “boom” sound. If there is an irregular sound, such as “sizzle” sound, “ho Luo” sound, “cha-ching” sound or “rustle”. The sound may indicate a bearing problem.
- Temperature monitoring: Continuous recording of temperature changes during bearing operation. Under normal circumstances, the bearing temperature will gradually increase and reach a stable state after 1-2 hours. If the temperature rises sharply, it indicates that there may be a problem with the bearing.
- Lubricant Condition Inspection: Samples of the lubricant are analyzed for dirtiness and the presence of foreign matter or metal powders. If the lubricant is in poor condition, it may indicate a bearing problem.
- Vibration signal analysis: Using a special bearing vibration meter, the magnitude and frequency distribution of the vibrations are measured. Through the amplitude value diagnostic method, probability density diagnostic method and other methods, the abnormal condition of the bearing can be inferred.
- Insulation performance check: Use an insulation resistance meter to measure the insulation resistance of the bearing. Connect the E end of the meter to the rotating shaft, and the insulated part of the bearing (e.g. outer ring) is covered with aluminum foil and then connected to the L end of the meter to measure the insulation resistance between the rotating shaft and the bearing housing or motor end cap. If the insulation resistance is lower than the standard value, it may indicate an insulation problem in the bearing.
Choosing TFL Insulated Bearings
If you want to choose the right insulation bearings with peace of mind, facing a variety of brands and models, and do not know how to choose, come to TFL Bearing Company. TFL Bearing has a wide range of products and can provide you with thoughtful counselling services to help you make your selection.
TFL Product Line Overview
TFL insulated bearings product line contains many types, the agent brand includes SKF, KOYO, NTN and so on. We can provide various types of insulation bearings, including ball bearings, angular contact bearings, spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, needle bearings, tapered roller bearings, precision bearings, etc. TFL insulation bearings guarantee the quality of the products, the fine insulation process, and a variety of categories for you to choose from.
After-sales service and support
Respect customers, understand customers, continue to provide products and services beyond customer expectations, and be a permanent partner of the customer, which is the concept we have always insisted on and advocated. Perfect service system, strengthen the pre-sale, sale, and after-sale service, responsible for customers, products, and our brand!
Conclusion
Insulated bearings are a type of bearing that can effectively solve the problem of shaft current corrosion. They have a wide range of application prospects and important technical value in modern industry. The electrical insulation performance realized through special process treatment not only improves the service life and reliability of the bearings but also reduces the equipment maintenance cost. With the continuous progress of technology and market expansion, insulated bearings will certainly play an important role in more fields.
Through this article, choose the right insulation bearings for your equipment and improve your productivity; come to TFL Insulation Bearings to consult and buy!
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main benefits of using insulated bearings?
The main benefit of using insulated bearings is to prevent current erosion of bearings and equipment, stop galvanic corrosion reactions, protect the life of bearings and equipment, and increase productivity.
- How do I know if my application requires insulated bearings?
The primary basis for determining whether equipment requires insulated bearings is the operating environment and operating conditions of the equipment, the type of current, and the potential galvanic reaction. For example, wet environments, high voltage conditions, and equipment susceptible to galvanic damage all require the use of insulated bearings.
- What is the difference between ceramic-coated and hybrid insulated bearings?
The main difference between ceramic-coated bearings and hybrid ceramic bearings lies in their structure and performance characteristics.
Ceramic coated bearings: the outer ring or inner ring of such bearings are coated with a layer of ceramic coating on the surface, usually selected with high hardness, wear resistance, good heat conduction properties of ceramic oxide materials, such as alumina and so on. The thickness of the coating is generally between 0.2mm~0.4mm to ensure sufficient insulation strength and wear resistance.
Hybrid ceramic bearings: The rolling bodies of these bearings are made of ceramic materials (e.g. silicon nitride), while the inner and outer rings are made of bearing steel. This structure allows the bearings to have good electrical insulation properties while maintaining high strength and wear resistance.
- How long do TFL insulated bearings typically last?
It is difficult to give an exact figure for the service life of insulated bearings. However, according to industry experience, the service life of insulated bearings can usually range from thousands to tens of thousands of hours under normal use and maintenance conditions. However, please note that this is only a general range; the specific life should be judged according to the use of the environment, lubrication status, load conditions and so on.
- Can TFL provide custom insulated bearing solutions for unique applications?
TFL Insulated Bearings can provide customized bearing solutions for unique applications.TFL Bearings has a full range of insulated bearings and maintains long-term stable cooperation with many well-known bearing companies. Tell us your needs, and we will select and customize the best quality insulation bearings for you!
