Materials for Electrically Insulated Bearings
Introduction
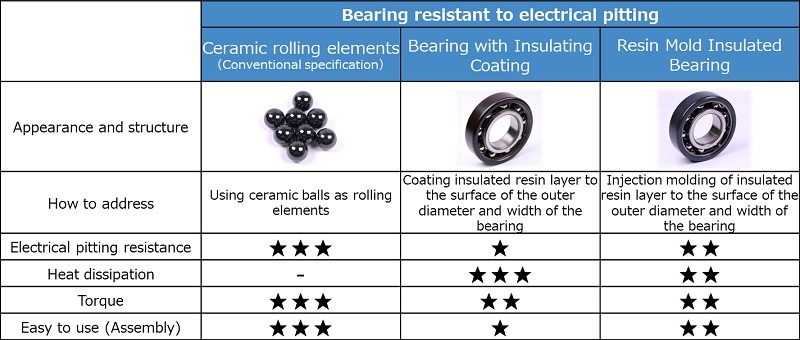
Electrically insulated bearings have additional insulating properties than normal bearings. Insulated bearing technology involves spraying insulating materials on the inner or outer ring of the bearing and using ceramic rolling elements. Thanks to their unique insulating properties, electrically insulated bearings play a significant role in industrial applications.
Common Materials for Electrically Insulated Bearings
Common materials used for electrically insulated bearings include ceramic materials such as alumina, zirconia, silicon nitride, rubber, and plastic.
Use of Ceramic Materials
The application of ceramic materials in insulated bearings is mainly reflected in their rolling bodies. Rolling bodies (balls or rollers) made of ceramic materials can significantly improve the insulating performance, high-temperature resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and other characteristics of bearings. Depending on the type of ceramic material, two main materials are used to manufacture ceramic rolling bodies: zirconium oxide (ZrO2) and silicon nitride (Si3N4). These materials have good corrosion resistance, are non-magnetic, and have electrical insulation and other properties.
Effectiveness of Polymer Coatings
Polymer coatings are coatings or paints made from polymer materials such as natural rubber, polyurethane, acrylic, and silicone. These materials are used on a wide variety of substrates, including metals and ceramics, because of their good adhesion and corrosion resistance. They are FDA-approved and have temperature resistance up to approximately 535°F (280°C). In insulated bearings, polymer coatings are sprayed or coated on the surface of the outer or inner ring of the bearing to provide additional insulation protection.

Advantages of Composite Materials
Composite bearing material is a kind of bearing material composed of a metal matrix and composite material layer. The composition of composite-bearing material mainly includes a metal matrix and composite material layer. The metal matrix is usually made of copper, aluminum, iron, and other metal materials with good thermal and electrical conductivity and can withstand large loads. The composite material layer is made of resin, fibre, and other composite materials with good resistance to wear and corrosion resistance. This double-layer structure makes the composite bearing material not only have the strength of the metal material but also has excellent performance of the composite material, can meet the use of a variety of complex working conditions, and is widely used in mechanical equipment, automotive, aerospace, and other fields.
Innovative Insulation Materials
With the gradual development of technology, some advanced bearing insulation coatings have emerged. Innovative bearing insulating materials include silicon nitride, silicon carbide, and ultra-high molecular weight polyethene (UHMWPE). These materials are widely used in various industrial applications due to their unique properties.
Nanotechnology in Insulation
The application of nanotechnology in insulating bearing materials mainly enhances the insulating and mechanical properties of bearings by adding nanoparticles to the material. Insulation materials are introduced with nanoscale particles through nanotechnology, and the physical and chemical properties of the materials are enhanced with increased durability and reliability. For example, a new type of insulating bearing is made by a specific synthesis process using a sol-gel method to prepare silica and aluminium trioxide sols, which are homogeneously dispersed in a polyamide acid solution. This bearing has excellent insulating properties and effectively prevents galvanic corrosion damage, improving its reliability and service life.
Stability at High Temperatures
The stability of bearing material in a high-temperature state is a key factor in determining whether it is suitable for use in high-temperature bearings because, under high-temperature conditions, many metals and materials undergo deformation, ablation, and other phenomena, resulting in bearings that do not operate properly. Among them, silicon nitride is the most widely used high-temperature resistant insulating material. However, at high temperatures, oxygen tends to oxidize the surface of silicon nitride to form SO₂. The thermal conductivity of SO₂ is not as high as that of silicon nitride, which can lead to problems with rising localized temperatures in bearings. At this time, the silicon oxide film formed on the bearing surface can well prevent the formation of silica and ensure the friction performance of the bearing and long-term running stability.

Methods for Enhanced Durability
With material selection and innovation, insulated bearing materials can enhance durability. For example, Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP) insulated bearings are lightweight, have good insulation properties, and have high mechanical strength. These properties contribute to the bearing’s overall durability.
Innovation of new composite materials: With the advancement of material science, new composite materials such as carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) are being used to manufacture insulated bearings. These materials have higher strength and better wear resistance while maintaining excellent insulating properties.
Applications of Insulated Bearing Materials
Electrically insulating bearing materials can be found in several industries, such as electric motors, wind turbines and rail transportation.
Role in Electric Motors
Materials used in insulated bearings in electric motors include ceramic coatings and ceramic rolling elements. One is to apply a ceramic coating to the outer or inner ring of the bearing, and the other is to use ceramic materials to process the rolling body. Both methods effectively prevent high-frequency currents from passing through the bearings, thereby preventing galvanic corrosion caused by the currents on the bearings and extending their service life. An example is a rotary kiln drive motor in a smelting plant. A rotary kiln in a smelting plant stopped because the drive motor shaft held up, triggering the overcurrent protection system. The technicians found that the shaft holding occurred because the shaft current eroded the bearings. This example illustrates the importance of using insulated bearings.
Applications in Wind Turbines
The application of electrically insulated bearing materials in wind turbines is mainly to ensure the safety and efficiency of the equipment. During the operation of wind turbines, the rotor inductively generates electric currents due to high-frequency rotation. Without the use of electrically insulated bearings, these currents will flow through the bearings and form a circulating current, causing the bearings to heat up or generate electric sparks, which in turn will damage the bearings. Particularly in large wind turbines, damage from shaft currents occurs mainly in motors powered by variable frequency power supplies with seat numbers 280 and above and in ordinary large and medium-sized high-voltage motors. Therefore, the use of electrically insulating bearing materials is necessary to prevent damage caused by current passing through the bearings.
Use in Railway Transportation
The application of insulated bearings in railroad transportation is mainly reflected in the traction motors of high-speed railways and electric locomotives. These bearings can withstand high-speed operation and heavy loads while preventing damage caused by current passing through the bearings to guarantee the safety and stability of the power supply system. In rail transportation, the main role of insulating materials is to protect electrical equipment and signalling devices, avoid interference and damage between them, and ensure the normal operation of trains. There are generally 3 types of insulated bearings used in traction motors: mixed ceramic bearings, ceramic sprayed bearings, and resin-coated bearings.
Cost-Effectiveness of Insulation Materials
Cost-performance analyses of bearing insulation materials need to be considered in a number of dimensions, including material performance, cost, application scenarios, service life, and maintenance costs. The following is a detailed analysis of the cost-effectiveness of bearing insulation materials:
Economic Benefits of Material Choices
- Ceramic Insulated Bearings: Because of the high cost of ceramic materials and the difficulty of processing, the price of ceramic-insulated bearings is relatively high. However, the high cost is offset to a certain extent by their excellent performance and long life, which bring better economic benefits and lower maintenance costs.
- Resin-Insulated Bearings: The relatively low cost of resin material makes resin-insulated bearings more competitive in price. However, it should be noted that resin materials may not perform as well as ceramic materials in high-temperature environments.

Properties of insulating materials
- Ceramic materials (e.g., zirconia, silicon nitride, silicon carbide): with extreme resistance to electrical breakdown and good temperature stability, they are ideal insulating materials. Silicon nitride ceramics, in particular, have excellent electrical insulation and are suitable for high-voltage environments.
- Resin materials (e.g., epoxy resins, polyimide): Resin materials also excel in insulating properties and can be used to meet different mechanical requirements by adding a variety of pigments and reinforcing agents.
- Alumina ceramics also have high-insulating properties and are widely used in electronics, electrical appliances, and aerospace, where high-insulating properties are required.
Low Maintenance Costs
Ceramic Insulated Bearings: Ceramic insulated bearings have high hardness, high strength, and low friction characteristics and will have a longer service life, reducing the cost of frequent bearing replacements and downtime and maintenance costs.
Resin-insulated bearings: Although resin-insulated bearings are less costly, they may have a relatively short service life, especially in high-temperature or high-load environments. As a result, their maintenance costs may be higher during long-term use.
Comparing Different Bearing Materials
Insulated-bearing materials also have a variety of materials; each material has its own characteristics. We can choose the right bearing material according to our use of the environment and the equipment requirements. The following is a comparison of different materials:
Ceramics vs. Metal Materials
The following is a comparison of the properties of ceramic and metallic materials:
| Items | Units | Bearing Steel | Stainless Steel | Ceramic Si3N4 | Ceramic ZrO2 | Ceramic Al 2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | g/cm3 | 7.85 | 7.9 | 3.20~3.30 | 6 | 3.95 |
| Coefficient of linear expansion | 10-6/ K | 10 | 11 | 3.2 | 10.5 | 8.5 |
| Young’s Modulus | GPa | 208 | 200 | 300~320 | 210 | 380 |
| Poisson’s ratio | -- | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.26 | 0.3 | 0.22 |
| Hardness | Hv10HRc | 700 62 | 66 | 1500~1800 75~80 | 1200 70 | 1800 80 |
| Bending strength | MPa | 2400 | -- | 800~1000 | 950~1200 | 300~500 |
| Fracture toughness | MPam-1/2 | 25 | -- | 6.0~7.0 | 10 | 3~4 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/mk | 30~40 | 15 | 35 | 2~3 | 30 |
| Special electrical resistance | Omm2/m | 0.1~1 | 0.75 | 1018 | 1015 | 1018 |
| Heat resistance | C | 120 | 300 | 800 | -- | -- |
| Corrosion resistance | -- | Low | Medium | High | High | High |
| Stress cycles(50% failed) | -- | 10×107 | -- | 10×107 | 10×105 | |
| Nonlubrication friction | -- | High | High | Low | -- | -- |
| Magnetism | -- | magnetic | magnetic | non- magnetic | non- magnetic | non- magnetic |
| Centrifugal force | -- | Very high | Very high | Very low | High | medium |
| Operate temperature increasing | -- | high | high | low | -- | -- |
| Size stability | -- | Low | Low | High | High | High |
| Conductivity | -- | conductor | conductor | insulator | insulator | insulator |
Polymer Coating vs. Non-Coated
Uncoated bearings are those that do not have any additional coatings and are made of metals such as steel or bronze. Commonly used in situations where long-lasting performance and durability are required. Coated bearings are bearings to which a layer of material, such as PTFE, ceramic or polymer, has been added to the inner and outer rings. Coated bearings are used where loads are extreme and engine rebuild times are short. Here is a detailed comparison of them:
| Criteria | Friction Reduction | Wear Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Tolerance | Load Capacity | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coated Bearings | Superior friction reduction due to specialized coatings. | Enhanced wear resistance,longer lifespan. | High corrosion resistance,suitable for harsh environments. | Better tolerance to extreme temperatures. | Higher load capacity due to surface strength. | Longer lifespan,fewer replacements. |
| Uncoated Bearings | Standard friction levels, may require lubrication. | Lower wear resistance,more frequent replacements needed. | Lower corrosion resistance,prone to rust and degradation. | Standard temperature tolerance,may fail in extremes. | Standard load capacity,may deform under high loads. | Shorter lifespan,frequent replacements needed. |
Use of Composites in Various Applications
Bearing composites are widely used in several fields due to their unique properties and advantages. The following are applications of bearing composites in certain fields:
- PEEK is a slide bearing commonly used self-lubricating polymer material with a room temperature coefficient of friction of 0.48, wear rate of 14 × 10-6mm3/N-m, a melting point of about 344 ℃, and glass transition temperature of about 143 ℃. Often modified to create a more comprehensive performance of PEEK composite plain bearings. PEEK composite friction coefficient is small, low wear rate, the manufacture of PEEK composite plain bearings self-lubricating performance is excellent, with good temperature characteristics. In addition, its mechanical properties, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, lightweight characteristics, and dimensional stability are outstanding and have been used on many occasions, such as in compressors, water pumps, magnetic pumps, and other equipment with plain bearings in the application.
- Carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) composites are widely used in the manufacture of bearing gears due to their high strength, lightweight, and good wear resistance. This material combines the high strength of carbon fibre and the easy processability of plastic, resulting in better performance and longer service life of bearing gears when subjected to high loads. In practical applications, CFRP composites have been widely used in aviation, automotive, wind power, and other fields. For example, in wind power generation, the gearboxes of large wind turbines need to withstand extremely high torque and rotational speed, and the application of CFRP composites can effectively improve the bearing capacity and service life of the gearboxes.
Conclusion
To summarize, different materials for electrical insulation bearings have different characteristics, and choosing the right bearing material has a great impact on insulation performance, bearing and equipment stability, improving productivity, etc. TFL Insulation Bearings has a complete range of bearing materials, and the agent brands include SKF, KOYO, NTN, etc. We can provide various types of insulation bearings, including ball bearings, angular contact bearings, spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, precision bearings, bushings, thrust bearings, etc. We can provide various types of insulation bearings, including ball bearings, angular contact bearings, spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, precision bearings, bushings, thrust bearings, linear bearings, single and double row bearings, inch bearings. We help you choose suitable and correct insulated bearings.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What materials are best for electrically insulated bearings?
Materials used for electrically insulated bearings include plastics, ceramics, and fibreglass, the most suitable of which include silicon nitride ceramics and zirconia ceramics. Both of these materials have good insulation and corrosion resistance and can meet the needs of electrical insulation bearings.
- What are the benefits of using insulated bearing materials?
Insulating bearing materials increase bearing life and reliability while reducing maintenance costs and increasing productivity. Because of their advantages, insulated bearings are used in a wide range of motors and power generation equipment, making them an economical and effective solution.
- How does the cost-effectiveness of different insulation materials compare?
The cost-effectiveness of different insulating materials depends on a number of factors, such as performance, processing difficulty, service life, and market demand. Comparison of the cost-effectiveness of different insulating materials requires comprehensive consideration of a number of factors. When selecting insulating materials, they should be weighed and selected according to the specific application scenarios and needs.
- How do insulation materials enhance durability?
The durability of insulating bearing materials can be improved by selecting high-performance materials and composites, improving manufacturing processes, using more advanced plasma spraying technology, and optimizing heat treatment processes. Proper use and regular maintenance of bearings can also be improved, as can continuous research and development of new materials, such as advanced polymers, composites, and special coatings.
- In which industrial fields are electrically insulated bearings most widely used?
Electrical insulating materials have a wide range of applications in a number of industrial fields, including but not limited to wind power, rail transportation, industrial motors, new energy vehicles, hydroelectric power generation, photovoltaic power generation, and so on.
