What is a Bearing
Speaking of the origin of bearings, this has to be traced back to the ancient Egyptian period. The early form of linear motion bearings consisted of a row of wooden poles placed under a skid. This technique may be traced back to the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, although there is no clear evidence yet. Modern linear motion bearings use a working principle, but sometimes balls are used instead of rollers.
Early-stage
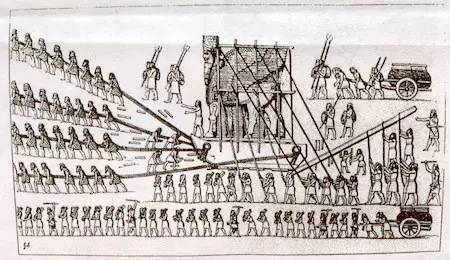
From heavy-duty wheel axles and machine tool spindles to precision watch parts, rotating bearings are required in many cases. The simplest rotary bearing is a bushing bearing and just a bushing sandwiched between the wheel and the axle. This design was subsequently replaced by rolling bearings, which replaced the original bushings with many cylindrical rollers, each of which was like a separate wheel. The first rolling bearing with the cage to be put into practical use was invented by watchmaker John Harrison in 1760 to make the H3 chronograph.
In the 17th century, Galileo made the earliest description of “fixed ball” or “cage ball” ball bearings. But for a long time afterward, the installation of bearings on the machine has not been realized. The first patent on the ball groove was in 1794. An iron manufacturer named Philip Vaughan of Carmarthen in Wales used ball bearings as axle bearings for carriages. From then on until the 1950s and 60s. In the age, ball bearings were widely used in children’s carousels, propeller shafts, machine gun turrets on warships, armchairs, and bicycles.
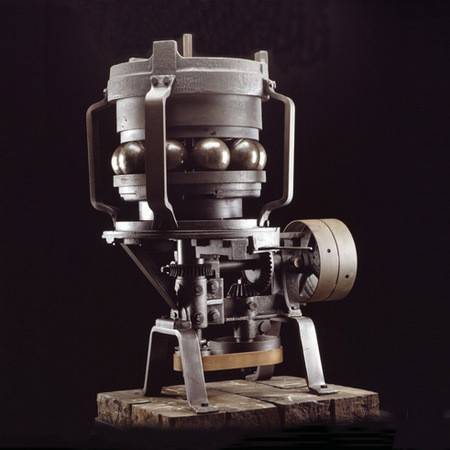

In 1883, FAG founder Friedrich Fisher proposed using suitable production machines to grind steel balls of the same size and accurate roundness. This laid the foundation for the creation of independent bearing industry.

In 1895, Henry Timken designed the first tapered roller bearing, after three years to obtain a patent and Timken (Timken) company.
In 1907, Sven Winquist of the SKF bearing factory designed the earliest modern self-aligning ball bearing.
Although the bearing was invented for some time, the industrialized production of the bearing was born out of nothing, just started and quite immature.
Growth period
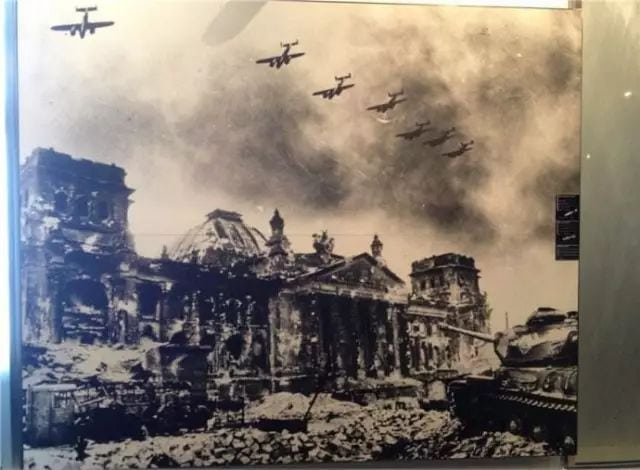

The two world wars stimulated the development of the military industry, the bearing military industry’s increasingly prominent position, coupled with the rapid development of science and technology, the short-term stability after the First World War, and the urgent need for munitions during the Second World War, prompted the rapid growth of the world bearing industry and the increase in bearing varieties. It is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, airplanes, tanks and armored vehicles, machine tools, instruments, meters, bicycles, sewing machines, etc.
During the Second World War, with the modernization of the means of war, people’s understanding and emphasis on bearings have reached unprecedented heights. All countries are in urgent need of bearings and are eager to establish a bearing industry. Therefore, many bearing factories have appeared in various countries. . This can be seen only from the selection of points when the Allied forces attacked the German Nazis. Large-scale cluster bombing, destroying the morale and economy of the enemy in one fell swoop, was a typical tactic of the Second World War. When driving to Germany to attack targets, the Allies believed that to weaken the enemy’s combat effectiveness, it was necessary to bombard German submarine factories and bases, aircraft factories, bearing factories, oil refineries, synthetic rubber factories, and vehicles. The bearing factory was set as a key bombing target, and the small town of Schweinfurt, where the German bearing factory was concentrated, was subjected to large-scale bombing twice in August and October 1943. Performing the bombing mission is the U.S. Ace Air Force Eight. Nazi German Military Supplies Minister Albert Schupé admitted that the bombing in August reduced German bearing production by 38%, while the results of the bombing in October destroyed 65% of bearing companies.
Development period
With the rapid development of high and new technology such as aerospace, nuclear industry, electronic computers, photoelectromagnetic instruments, precision machinery, etc., the world bearing industry, which reflects the level of contemporary science and technology, has entered a comprehensive, innovative manufacturing technology, rapidly developed varieties, and greatly improved performance and accuracy. , A new historical period of increasing maturity and perfection.
There are all kinds of bearings in this period, and their uses are all-encompassing. At present, there are tens of thousands of bearing types. Extra-large bearings are as large as 38 meters, and miniature bearings are as small as a few tenths of a millimeter. There are traditional single-row, double-row, and multi-row ball bearings, roller bearings, Needle roller bearings, tapered bearings, non-lubricated bearings, self-lubricating bearings, angular contact bearings, transmitter bearings, universal joint bearings, ultra-thin-wall bearings, hub unit bearings, air bearings, linear bearings, superconducting bearings, magnetic suspension Bearings and so on.

The bearing industry has become a big climate. Like parts and components, small bearings already have an exclusive market that is quite large and cannot be underestimated. The bearing trade has ushered in its heyday.
Bearings are actually by our side, and the amount is amazing.
Take a car as an example. A car generally uses 100 to 150 bearings. If there is no bearing, the wheels will rattle, the gears of the gearbox will not mesh, and the car will not be able to drive.
There are bearings, cars, railway vehicles, airplanes, washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, vacuum cleaners, photocopiers, computers, and even satellites flying in distant space. Bearings have played an important role in improving mechanical operation efficiency and energy saving. Regrettably, because the bearing runs silently inside the machine, it is rare for everyone to see the true face of the bearing directly. But the bearing is indeed an important part of maintaining the machine’s stability and performing its function.
Bearing in English is “Bearing” “Bear” has the meaning of supporting and bearing.
Bearings have two key functions:
- Transfer motion, i.e. they support and guide components which turn relative to one another
- Transmit forces
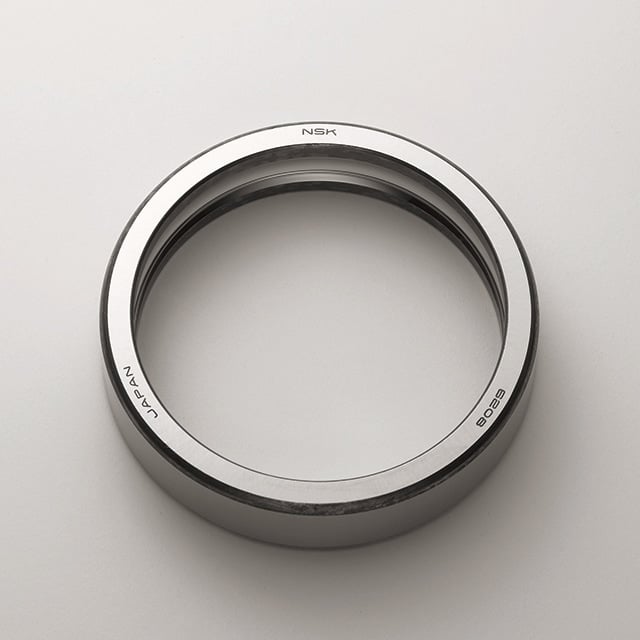
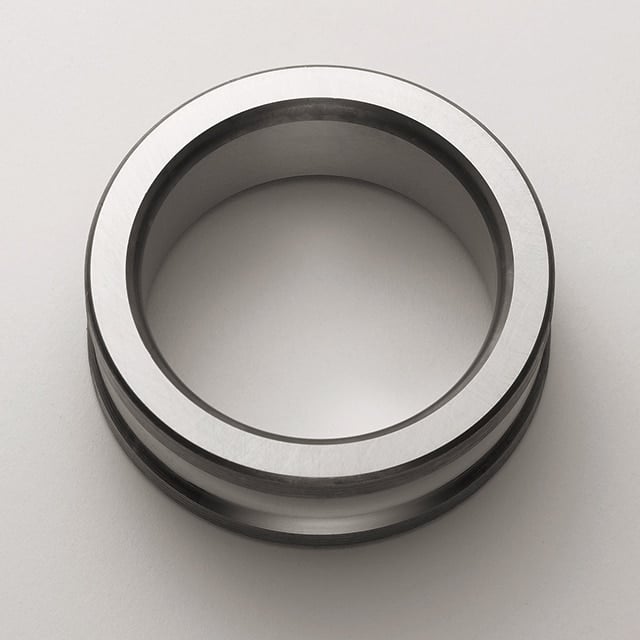
Inner Ring / Outer Ring
The inner and outer rings are typically made from high-purity, chrome alloy steel. This material has the necessary hardness and purity, important factors for high load ratings and long service life.
The raceways are hardened, ground, and honed.
Special materials such as ceramic and plastics are also produced. Although plastics cannot withstand extremely high temperatures, they are considerably lighter than steel, making them invaluable in the automotive industry, where every ounce matters.

Outer ring

Inner circle
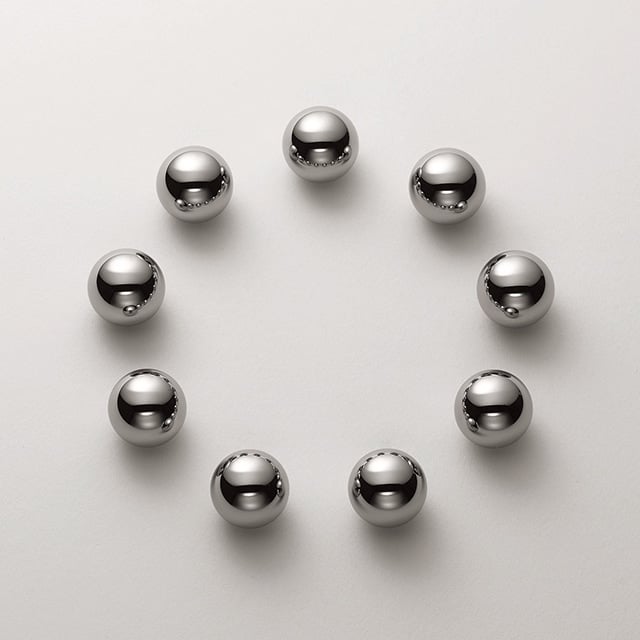

Rolling element
Rolling elements can be balls, rollers, cones, spheres, or needles. They are usually made from a special high-purity, chrome alloy steel. Special materials such as ceramic and plastics can also be produced.
The rolling elements roll on the raceways of the rings and are separated and guided by the cage.

Cage
The cage is responsible for keeping the rolling elements separated while guiding them in motion. The materials used include steel, brass, and plastic. Solid metal cages can be produced using machining techniques, while pressed cages are made from sheet metal. Similarly, plastic cages can be machined from solid plastic or injection molded.
- The basic function of the bearing is to “reduce mechanical friction“. There are three major benefits of reducing friction, namely,
- Improve the working efficiency of machinery.
- Extend the service life of the machine.
- Prevent seizure and reduce mechanical failure.
- Bearings can reduce friction and improve transmission efficiency, which is conducive to energy saving. This is why people often say “bearing environmental protection”.
Bearing Type List
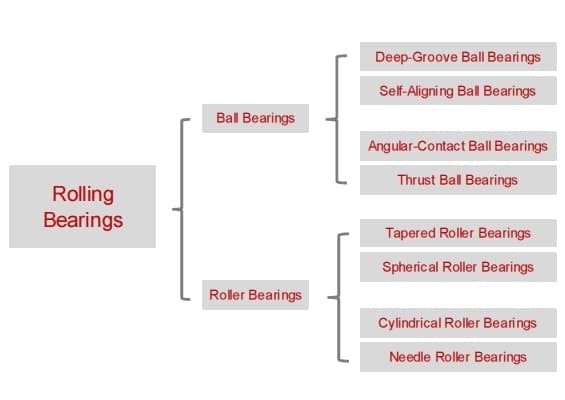
Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings utilize balls as the rolling elements. They are characterized by point contact between the balls and the raceways. As a rule, ball bearings rotate very quickly but cannot support substantial loads.
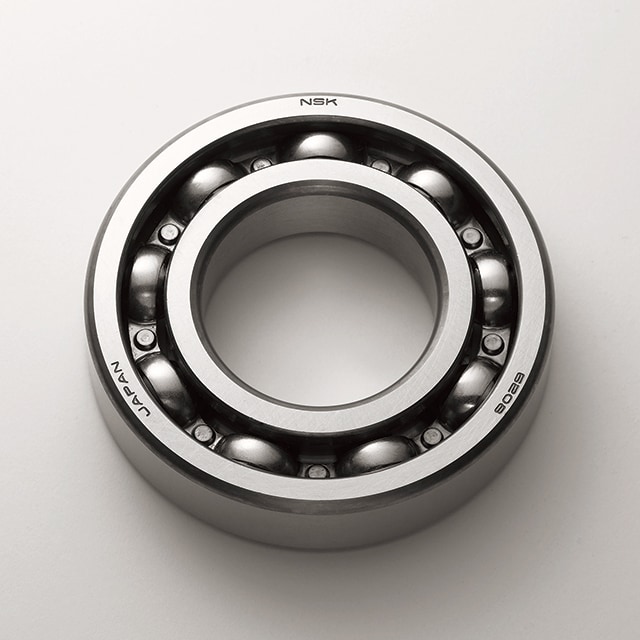

Deep-Groove Ball Bearings
The most commonly used bearings are Deep-Groove Ball Bearings. Thanks to their simple design, they are easy to maintain and not as sensitive to operating conditions; thus are used in a wide range of different applications.
In addition to radial forces, they absorb axial forces in both directions. Their low torque also makes them suitable for high speeds.
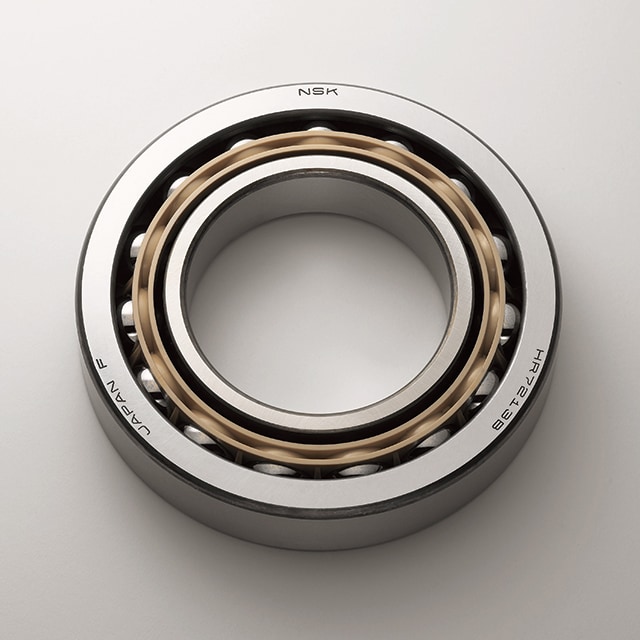

Angular Contact Ball Bearings
A contact angle characterizes Angular Contact Ball Bearings. This means that forces are transferred from one raceway to the other at a particular angle.
Angular contact ball bearings are therefore suitable for combined loads, where high axial forces have to be transferred in addition to radial forces.
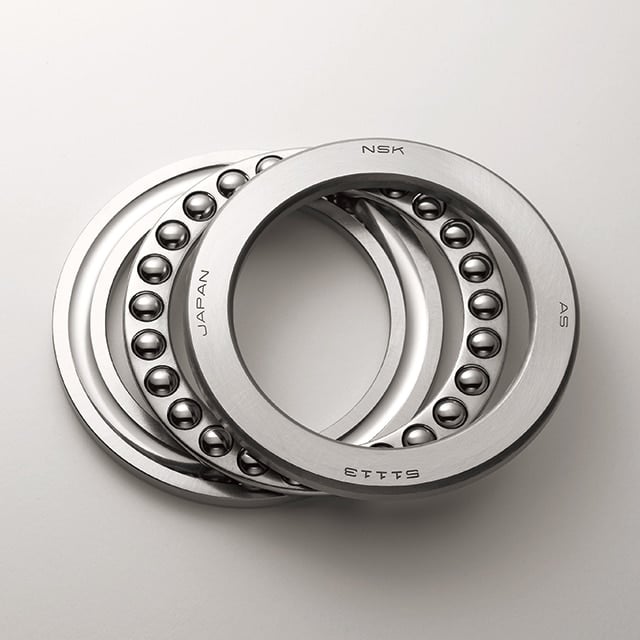

Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust Ball Bearings consist of two bearing discs with raceways for the balls.
Thrust ball bearings were developed solely for absorbing axial forces in one direction, meaning they can locate the shaft axially in one direction.
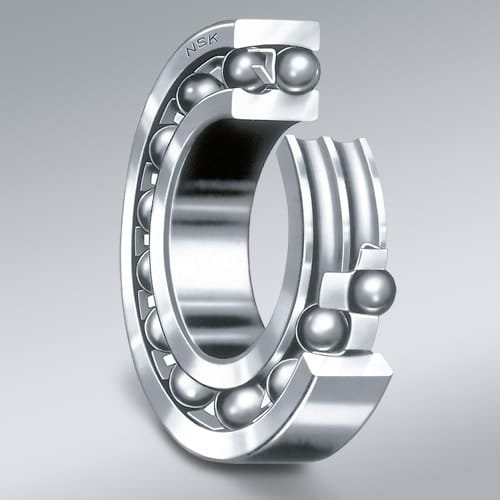

Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings include a double row of balls guided by a cage and double row inner ring raceway but have the special feature of a continuous spherical outer ring raceway allowing the inner ring/ball complement to swivel within the outer ring. This is what enables a degree of self-alignment in the application.
This type of bearing is recommended when the alignment of the shaft and the housing (misalignment) are a problem, and the shaft could deflect. Self-aligning ball bearings are most suitable for absorbing radial forces.
Roller Bearings
Roller Bearings are characterized by line contact. Line contact offers a higher load rating than ball bearings of the same size; however, the speed ability is lower than a ball-bearing due to the increased friction of a contact line.
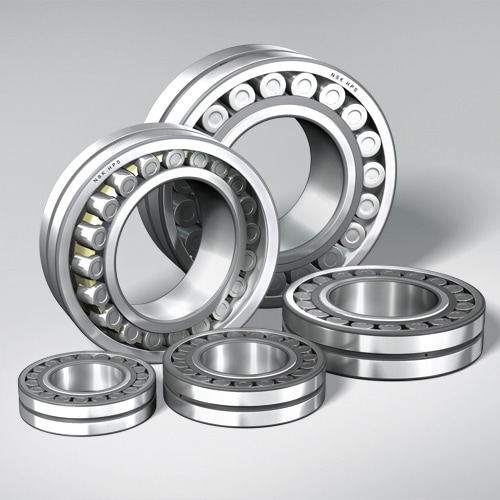

Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings are very robust and work on the same principle as Self-aligning bearings with the exception that they use spherical rollers instead of ball rollers allowing higher loads to be supported. This can compensate for misalignments between the shaft and the housing.
Spherical roller bearings are suitable for absorbing high radial loads and moderate axial loads.
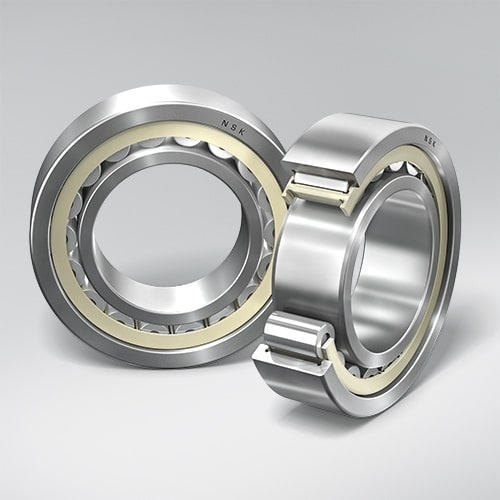

Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings use line contact between the rolling elements and the raceways, which optimizes the distribution of stress factors at the point of contact. This arrangement means that cylindrical roller bearings have a very high radial load rating.
Depending on the design, they may also be able to transmit limited amounts of axial loads.
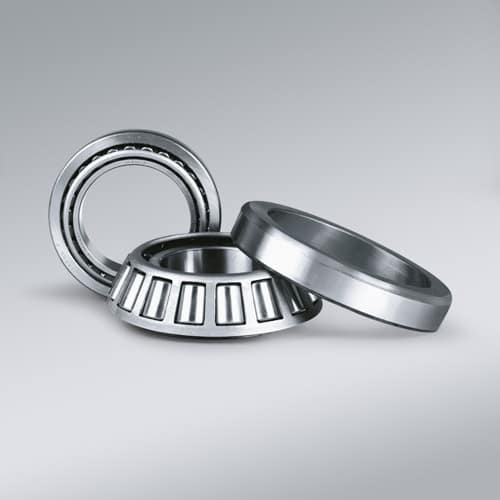

Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings have tapered raceways in the inner and outer rings with conical rollers arranged between them.
Due to the contact angle, tapered roller bearings can absorb high radial and axial forces in one direction.
Tapered roller bearings are often combined in pairs to support axial forces in both directions.
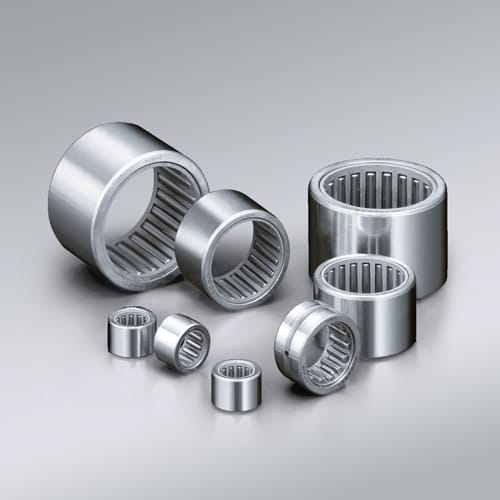

Needle Roller Bearings
Needle Roller Bearings are a special type of cylindrical roller bearing which contain long, thin rolling elements, known as needle rollers. The ratio of diameter to length is between 1:3 and 1:10.
Needle roller bearings have a high load rating and are only suitable for radial forces.
Size from 2 mm to 6 m
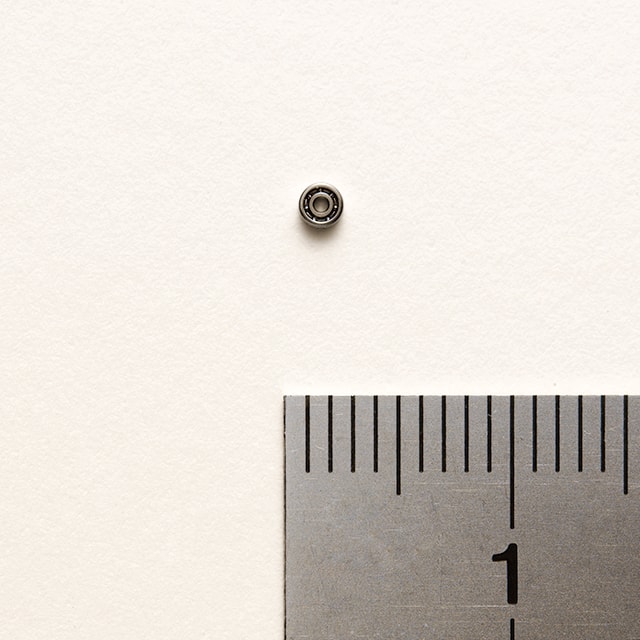

Size from 2 mm to 6 m
Bearings vary in size from small to large. The smallest “miniature bearing” in the world has an inner diameter of 0.6 mm × an outer diameter of 2.0 mm × a thickness of 0.8 mm and is used in micro motors. With an outer diameter of 6 meters and a weight of more than 15 tons, the large bearing is used in large-scale shield machines for tunnel excavation. This type of shield machine was used when digging a cross-sea tunnel under the Strait of Dover, which connects Britain and France, and this type of large bearing was used.
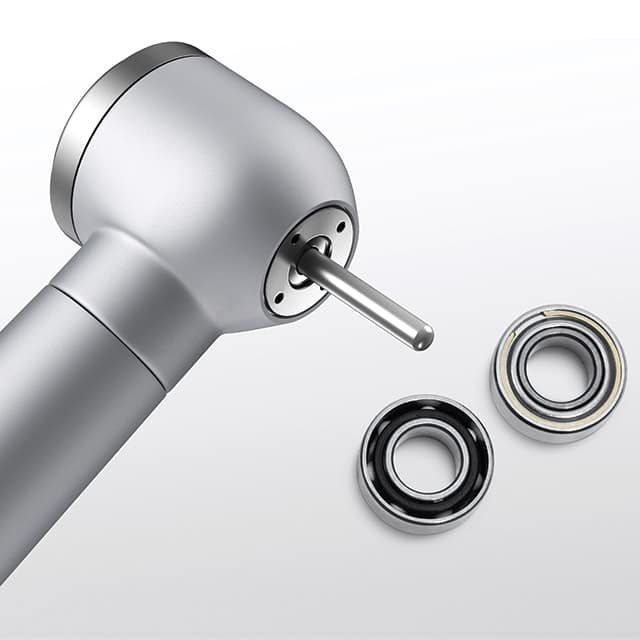

400,000 Revolutions per Minute
Bearings can run at very high speeds, which is common in applications such as dental drills. These drill bits use tiny high-precision ball bearings and rotate at up to 400,000 revolutions per minute.
These extremely high speeds and absolute accuracy almost eliminate the vibration of the dental drill. In addition to being a fascinating aspect from a technical point of view, it should also be a relief for patients, who can rest assured that they will receive safe and quiet treatment.
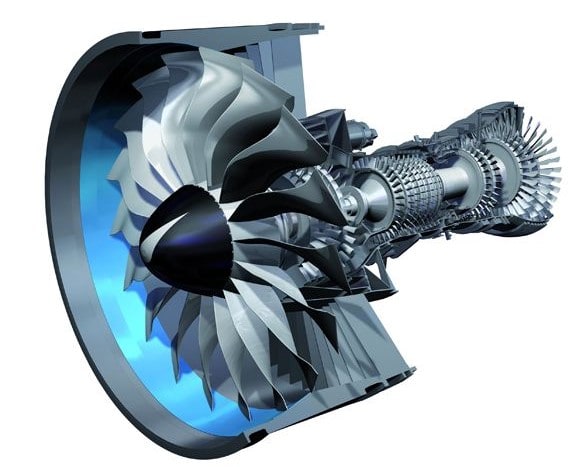

Bearings Enable Flight Speeds of 360 mph
The main shaft bearing for the jet engine V2500 of an international airliner has a rolling speed of 160 meters per second, equivalent to 580 kilometers per hour. It is precisely because of high-performance, high-speed bearings that the engine can run safely for a long time and safely send passengers to all parts of the world.

Vibrations of Less than 100 Nanometers
A machine’s precision rests on the accuracy of its bearings. A bearing supports each end of a rotational axis. The machine then operates precisely, even if there is a long run-out from the center of the axis or running at high speed. For example, high-precision bearings with minimal vibrations of less than 100 nanometers* are used for computer drives.
(*1 nanometer is a thousand millionth of a meter).

Revolving in Space for 15 Years
The development of the universe is also inseparable from bearings. Weather forecasts, satellite radio, television signals, and car satellite positioning information are all provided by artificial satellites orbiting the earth. The satellite is equipped with a gyroscope to maintain the satellite’s attitude and head, and the gyroscope is equipped with ultra-precision bearings. This kind of bearing can work continuously in space for 15 years.

The world from minus 253 degrees to minus 500 degrees
The bearing in the liquid fuel pump of the aerospace rocket is the bearing with the lowest temperature. This kind of bearing works in liquid hydrogen at minus 253°C. The bearings used in high-temperature environments are typically represented by special high-performance bearings in medical CT scanners. In X-ray vacuum tubes with temperatures as high as 300 to 500°C, the bearings can continue to run, playing a role in protecting our health.
Finally, introduce the issues facing the development of bearings.
- First of all, it is more “energy-saving”. The smaller the machine, the smaller the parts that make up the machine. Moreover, the smaller and more precise the machine, even the slightest friction may cause malfunctions. In addition, from a global perspective, no matter how small the machine is, the total amount of energy loss is quite large. Therefore, in order to be more energy-saving, bearings must also be developed in the direction of further reducing friction.
- Secondly, it is more “environmentally friendly”. The bearing is placed in the machine, which can also reduce the exhaust gas emissions of automobiles, so as to achieve environmental protection. In addition, most bearings are made of steel materials that do not contain harmful chemical substances, so they can be recycled and reused, and the smelting process is relatively simple. Therefore, bearings are very good renewable and reusable products.
- Third, it is more comfortable. The purpose of manufacturing machinery is to make human life more comfortable. In the past, machinery was mainly used to improve production efficiency. In the future, machinery will play a greater role in social life and personal life such as education, medical treatment, and entertainment. For this reason, new and higher requirements will be put forward for the function and use of the bearing.
