Insulated bearings for traction machines
Introduction: The Importance of Insulated Bearings in Traction Machines
Current erosion problems are mainly concentrated in tractor motor parts, especially in critical components such as bearings and windings, where shaft currents passing through the bearings penetrate the very thin oil film, which generates electric sparks, leading to localized melting damage of the contact surfaces. The emergence of insulated shaft bearings for traction machines solves this problem. As a principle, the electrically insulated bearing prevents galvanic corrosion by cutting off the current circuit.
How Insulated Bearings Work
The principle of insulated bearings is mainly through a layer of insulating coating on the surface of the bearing, the thickness of which is about 50-200 μm, or the rolling body is made of ceramic to prevent galvanic corrosion damage when the current passes through the bearing and to protect the internal structure of the bearing from damage.
The basic structure of insulated bearings
The basic structure of an insulated bearing consists of an inner ring, an outer ring, a rolling element, and a cage, which is similar to the structure of a non-insulated bearing. The difference lies in the manufacturing process, which adopts a special spraying process to make the bearings have the function of preventing electrical corrosion.
Introduction to Insulation Materials for Traction Motor Bearings
There are roughly three types of insulated bearings for traction motors, namely, resin-coated bearings, hybrid ceramic bearings, and ceramic-sprayed bearings.
- Resin-coated bearings: This kind of bearing is currently used with more PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) insulated bearings, whose outer surface of the outer ring is coated with PPS insulating resin to prevent the bearing from galvanic corrosion. Its advantage lies in excellent electrical insulation performance and low price. However, this kind of bearing is unsuitable for machinery where the bearing temperature rises sharply or when there are strict requirements for the change of overload, so it is mostly used in motors where the conditions are more lenient.
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings: Only the rolling body parts in this type of bearing are made of ceramic materials, also known as hybrid ceramic ball bearings. It uses engineering ceramics as materials with good mechanical and thermal properties, such as sufficient strength, stiffness, hardness, fracture, impact resistance, high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, etc., which are better than metal materials. The main ceramic materials suitable for making bearings are silicon nitride (Si3N4), zirconium oxide (ZrO2), and aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Among them, silicon nitride has become the preferred material for ceramic bearings because of its superior comprehensive performance.
- Ceramic-sprayed bearings: These are insulated by a ceramic coating with a thickness of 50 to 200 μm, which can resist electrical jump fires generated by voltages of 1,000 V. Thicker coatings can resist high-voltage discharges of more than 1,000 V. The coating maintains its insulating properties in wet environments.
Difference between insulated bearings and normal bearings
The main difference between insulated bearings and ordinary bearings is whether they are insulated and the process. Insulated bearings use a special spraying process in the bearing of the inner and outer ring surface, spraying high-quality coating, forming a layer of uniform thickness, strong adhesion of the coating, with up to 1000 megohms above the insulating impedance, and withstand more than 3,000 volts of breakdown voltage ability. Ordinary bearings do not have this insulation treatment and are easily damaged by galvanic corrosion.
Role of Insulated Bearings in Various Traction Machine Applications
Insulated bearings are used in a wide range of applications in modern industry, such as electric locomotives, high-speed trains, industrial motors, wind turbines, electric vehicle drives, and so on.
Applications in electric locomotives
Electric locomotives are characterized by high power, strong overload capacity, large traction force, and high speed. During the operation of electric locomotives, due to various reasons, such as grounding device failure, the oil film layer being destroyed, etc., the current may flow through the bearings through a non-normal path or produce electric sparks, resulting in a galvanic corrosion phenomenon. The use of insulated bearings in traction motor spindles or housings can cut off the path of current through the bearings and protect the equipment and bearings.
High-speed train traction systems
Magnetic asymmetry of the armature and rotor exists in high-speed train traction machines. This asymmetry generates current through the bearings, which leads to damage such as corrosion pits, melt marks, galvanic corrosion fine lines, discoloration, and wear on the bearing raceways and rolling element surfaces. High-speed trains run at high speeds, with large loads and large temperature variations, which require extremely high performance in terms of precision, reliability, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of the bearings. Insulated bearings can meet these special requirements and prevent galvanic corrosion damage, ensuring the smoothness and safety of high-speed trains.

Use in industrial motors
A power plant has installed two 200MW circulating fluidized bed air-cooled coal-fired generating units, each boiler equipped with two secondary fans. The motor, since the commissioning of the frequent occurrence of motor bearing vibration, motor running noise, and other problems, had no choice but to replace the motor drive end and non-drive end bearings many times, but less than three months after the operation of the repeated failures. Replacing them with industry-specific insulated bearings solved the problem of shaft current damage.
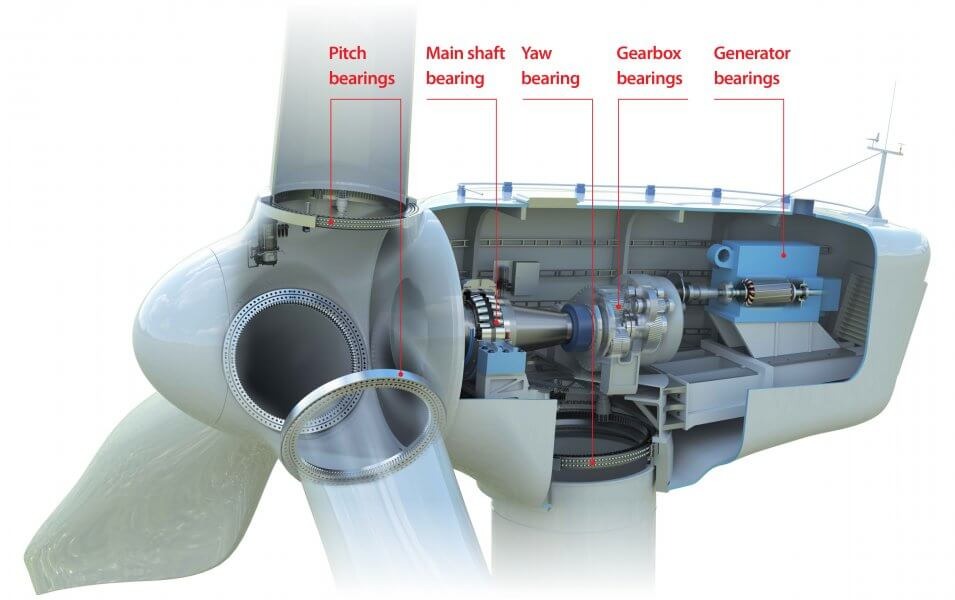
Importance in wind turbines
Shaft currents also exist in wind turbine generators that damage bearings and equipment. If insulated bearings are not used, due to the action of the shaft current, the bearing grease will be degraded and fail due to high temperature, and the bearings will be in an intermittent state of dry wear, leading to the burning of the bearings themselves and even sintered adhesion between the bearings and the shafts, and ultimately leading to the bearings falling apart and burning. Therefore, the bearing housing of the generator should be insulated.
Application of Drive Systems for Electric Vehicles
The popularization of new energy vehicles presents new challenges and opportunities for the bearing industry. As one of the core components of the electric drive system of new energy vehicles, TFL bearings need to withstand high-speed rotation, high temperature, high load, and other complex working conditions.TFL bearings, through technological innovation and material optimization, has successfully launched the new energy vehicle drive motor bearings with high-temperature resistance, wear resistance, and long service life. TFL-insulated bearings provide a strong force for the stability of the electric vehicle in high-speed driving and heavy-duty working conditions. TFL Insulated Bearings
Cost-benefit analysis of insulated bearings
The cost-benefit analysis of insulated bearings needs to consider the manufacturing costs, the resulting long-term maintenance costs, the improved operational reliability, and other economic benefits.
Initial investment and cost savings
Insulated bearings require a relatively high initial investment due to their special insulating coatings, material selection, and production processes. However, the insulating properties of bearings can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, extend service life, and increase productivity. Although the upfront cost of insulated bearings is roughly estimated to be several times or more than that of standard rolling bearings, the total cost is significantly lower, and the production uptime is correspondingly longer, an investment that often pays for itself in the long run through its superior performance and cost-saving effects.

Case Studies
Case 1:
The main centrifugal fan in the slag drying line of a major North American cement producer had a 1,200 hp DC motor with variable speed control between 750 and 1,800 r/min, and the motor needed to be replaced or reassembled every five weeks due to bearing problems. The bearings used were 6230M/C3 deep groove ball bearings. Galvanic corrosion was definitely the root cause of the bearing failure. In August 2012, 2 sets of 6230M/C3 deep groove ball bearings with ceramic rolling elements replaced normal bearings with steel rolling elements. When the motors needed to be repaired for other reasons in the summer of 2014, disassembly revealed that the bearings showed no signs of galvanic corrosion damage, and bearing life was extended from 5 weeks to over two years. Avoiding the cost of accidental shutdown and reinstallation resulted in an estimated savings of $47,100/year.
Case 2:
On a 288 kW AC motor-driven vertical roller mill, a cement plant in Southeast Asia experienced a long history of early bearing failures. Failures used to occur every 3 to 6 months, resulting in an average of 6 hours of incidental downtime and significant productivity losses. An analysis by the bearing manufacturer determined that the root cause of the failure was stray currents passing through the motor bearings. The solution was to install bearings with ceramic coating on the outer ring at the non-driven end and to install bearings with ceramic coating on the inner ring at the driven end. The bearings have been in operation for more than three years since 2015, with no failures noted, saving more than $68,000.
Key Considerations for Choosing the Right Insulated Bearings
Choosing the right insulated bearings can greatly increase productivity and reduce maintenance costs. Key factors to consider are load capacity, operating environment, and electrical insulation properties.
Mechanical properties and load capacity
The type of load is an important factor to consider. The types of loads that a bearing needs to be able to withstand include radial loads, axial loads, or combined loads. For example, if the equipment is mainly subjected to radial loads, such as pulleys, gear systems, etc., deep groove ball insulated bearings or cylindrical roller insulated bearings are usually selected, whereas equipment that is mainly subjected to axial loads, such as thrust ball insulated bearings or angular contact ball insulated bearings are usually more appropriate.
Lubrication conditions
The lubrication method has an important influence on the performance of the bearing, and the selection needs to consider the operating temperature, speed, and environmental conditions. Lubricating oil and grease are two common types of lubrication. For example, lubricants are suitable for high-speed equipment, and greases are suitable for low-speed, heavy-duty equipment; regular maintenance and replenishment of lubricants can extend the life of bearings.

Assessing the application environment
Environmental conditions also have an important influence on the selection of insulated bearings. For example, equipment operating in high-temperature environments requires the use of high-temperature-resistant bearing materials and lubricants, such as ceramic bearings or metal bearings with high-temperature-resistant coatings, whereas in low-temperature environments, bearings need to have good low-temperature performance, and if the bearings are going to be exposed to wet or corrosive environments, stainless-steel bearings or specially treated corrosion-resistant bearings need to be used.
Electrical insulation performance requirements
When selecting insulated bearings, the core requirement for electrical insulation properties is to withstand a voltage of at least 1000V. For higher voltage requirements, coatings can withstand over 3000V without electrical breakdown. The thickness of the insulating coating is typically 100 μm, but for applications that need to withstand higher voltages, the coating thickness can exceed 300 μm.12 The resistance of the insulating coating exhibits values of 2 × 10^5 to 210 ohms at DC voltages and 5 × 10^4 to 6 × 10^5 ohms at 50 Hz AC voltages. Insulated bearings are categorized into two designs, outer ring insulated and inner ring insulated, which are indicated by different designations, such as VL0241 for SKF and J20A34 for FAG.
Installation and Maintenance Guide for TFL Insulated Bearings
Correct installation can effectively ensure that the use and maintenance process of insulated bearings is error-free, thus enhancing their performance and service life.
Proper Installation Procedures
- Advanced mounting tools can avoid damage to the insulation bearings caused by improper tools and operation during mounting
- Before mounting the insulation bearings, please check whether the package is complete
- When assembling the motor, carefully check the fit dimensions of the bearings and the rotor shaft when the bearings are mounted, as well as the fit dimensions of the bearing outer ring and the holes in the end cover
- Control the amount of oil in the bearings and bearing housings
- Care must be taken for bearings with insulated outer rings to ensure the insulation is intact.

Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions
- The shaft and bearing bore fit too loose and is commonly known as the “walking inner ring.” Due to the shaft and bore selection of the fit being too loose, the shaft and bore surface slid, causing heat and damage to the insulation bearing. The solution is to select the appropriate fit size to ensure that the shaft and bearing bore fit tightly.
- Cracks caused by friction heat between the end face of the inner ring and the shaft shoulder: When “walking the inner ring,” the contact surface between the end face of the inner ring and the shaft shoulder is tiny, and the temperature is higher, resulting in thermal cracks. The solution is to ensure that the inner ring end face and the shaft shoulder are properly matched, avoiding over-tightening or over-loosening.
- Adhesion between the shaft and the surface of the bore: “Walking the inner ring” melts the surface metal and creates adhesion. The solution is to control the temperature during installation and avoid high temperatures.
- Hammer directly strikes insulation bearing installation: using a hammer to directly strike the inner ring or outer ring end face makes it easy to damage the bearing. The solution is to use professional bearing dismantling tools and avoid direct hammering.
Tips for extending the life of insulated bearings
The keys to extending the life of insulated bearings are proper installation, keeping the environment clean, adequate lubrication, avoiding strong shocks, regular maintenance, and condition monitoring. Failure to follow installation and maintenance requirements will result in equipment failure and constitute a major safety hazard. Therefore, correct lubrication and maintenance are very critical, correct installation and use are indispensable, and then make full use of the existing condition monitoring equipment escort so that your insulated bearings have a longer life.
Choose TFL Insulated Bearings to Enhance Traction Machine Performance
TFL-insulated bearings typically have an insulation thickness of 100μm and can withstand voltages of up to 1000V DC, effectively preventing the galvanic corrosion effects of induced currents on the bearings. We are very confident in our technology and performance advantages, bringing high practical value and considerable long-term benefits to our customers.TFL insulated bearings have won the trust and recognition of our customers with superior quality and comprehensive customized after-sales service. Come and contact us!
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are insulated bearings used for in traction machines?
The use of insulated bearings in traction machines is mainly to prevent damage caused by the passage of electric current through the bearings, especially at high speeds and under heavy loads. The insulated bearings can withstand high speeds and heavy loads to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
- How do insulated bearings improve the performance of electric motors?
Insulated bearings improve motor performance by avoiding the galvanic effect of induced currents on bearings and preventing current damage to grease rolling elements and raceways.
- What materials are used to make insulated bearings?
Insulated bearings are manufactured from materials with excellent electrical insulation properties. These materials are usually ceramics, such as alumina or silicon nitride, inserted between the bearing’s inner and outer rings.
- How to maintain insulated bearings effectively?
The keys to effective maintenance of insulated bearings are keeping them clean, ensuring proper lubrication, paying attention to seal protection, replacing worn parts on time, accurately adjusting bearing clearances, and equalizing load distribution.
- Which insulated bearing types are suitable for traction machines?
Three main types of insulated bearings are suitable for traction machines: combined ceramic bearings, ceramic-coated bearings, and resin film bearings.

