Comprehensive guide to deep groove ball bearings
Introduction:
Deep groove ball bearings are components of modern industrial workshops and play a key role in many mechanical systems. From daily household appliances to advanced industrial equipment, deep groove ball bearings are used everywhere to provide equipment with smooth and reliable operation. Whether you’re an engineering professional or a hobbyist interested in mechanical principles, use this guide to learn about deep groove ball bearing construction, materials, and diverse applications and how to choose the right bearing product.
What is a deep groove ball bearing?
Deep groove ball bearing is a kind of widely used rolling bearing, which is characterized by small frictional resistance, high speed, and ability to withstand radial load or radial and axial at the same time role of combined load. Deep groove ball bearings are usually used in small power motors, automobile and tractor gearboxes, machine tool gearboxes, general machines and tools.
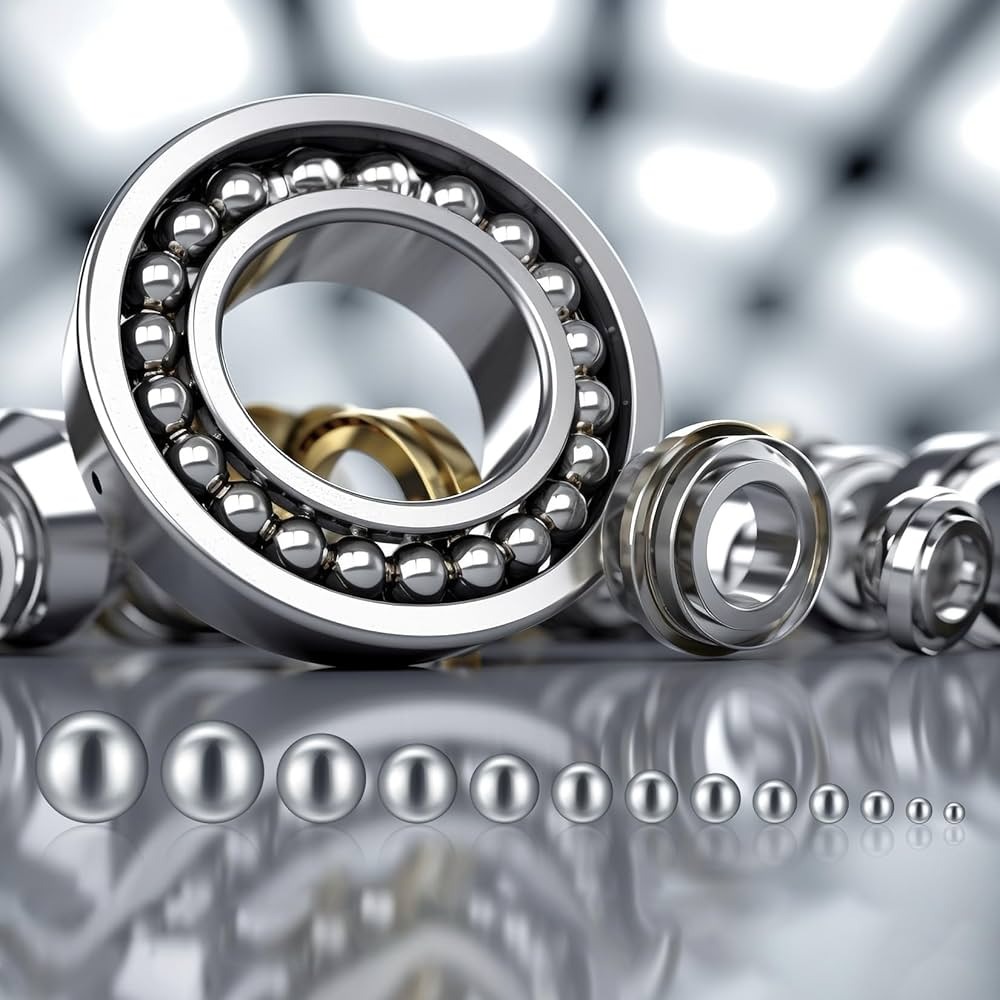

Definitions and basic structure
Deep groove ball bearing composition is a widely used rolling bearing, and its basic structure consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a group of steel balls and a group of cage compositions. Deep groove ball bearing is characterized by small frictional resistance and high speed, can withstand radial or radial-axial at the same time as the joint load, and can also be used to bear the axial load on the machine parts.
Working Principle
Deep groove ball bearings are mainly subjected to radial loads but can also be subjected to radial and axial loads. When deep groove ball bearings are subjected to radial loads only, the contact angle is zero. A deep groove ball bearing with a large radial clearance can withstand a large axial load. Deep groove ball bearings have a very low coefficient of friction and high limiting speeds, making them suitable for high or even very high-speed operation. They are very durable and do not require frequent maintenance.
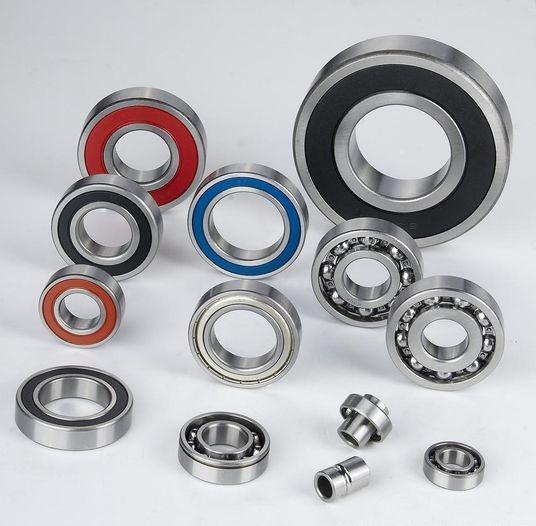
Types of deep groove ball bearings
There are various types of deep groove ball bearings, mainly including the following:
Open deep groove ball bearings: These bearings are mainly used to withstand radial loads but can also withstand smaller axial loads. Their axial displacement is limited to the range of axial clearance, and the inner ring can be tilted relative to the outer ring.
Deep groove ball bearings with dust cover: including single-sided and double-sided bearings with dust cover, there is a gap between the dust cover and the inner ring retaining edge. The limiting rotational speed is the same as that of the open deep groove ball bearings, but the seal is better.
Deep groove ball bearings with seals: including single-sided bearings with seals and double-sided bearings with seals. Seals and the inner ring retaining edge are contact or non-contact. The contact sealing effect is good, but the friction resistance and speed limit are low.
Deep-groove ball bearings with stop grooves in the outer ring: This type of bearing can simplify the axial positioning of the bearing in the housing bore after the stop ring is fitted.

Common materials (steel, ceramics, etc.)
Commonly used materials for deep groove ball bearings include the following:
Chromium steel: Chromium steel is one of the most commonly used materials for deep groove ball bearings, which has excellent wear and high-temperature resistance and is suitable for high-speed rotation and high-load mechanical equipment.
STAINLESS STEEL: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and high temperatures and is commonly used in machinery and equipment in the food and medical industries, especially in wet and corrosive environments.
High-carbon chromium-molybdenum steel: This high-strength alloy steel, with high strength and toughness, is suitable for high loads and high-speed mechanical equipment, such as bearing components in automotive, aerospace and other fields.
Ceramics: Ceramic materials such as alumina ceramics and silicon nitride oxide ceramics are characterized by high strength, hardness, and low coefficient of friction, making them suitable for high-speed, high-temperature, and high-precision application scenarios.
Plastic: Plastic bearings such as PEEK, PI, and other engineering plastics are suitable for applications with special weight and cost requirements.
Properties and benefits of each material
Carbon and Bearing Steels: Carbon and bearing steels (e.g., GCR15 or AISI 52100) are commonly used to manufacture rings and balls for deep groove ball bearings. These materials are heat-treated to provide excellent strength and wear resistance and are suitable for high load and high-speed conditions.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel materials have excellent corrosion resistance and are commonly used in wet or chemically corrosive environments. Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings can extend service life and reduce maintenance requirements.
Plastics and Ceramics: Plastic and ceramic materials such as alumina ceramics and silicon nitride ceramics are characterized by high strength, high hardness and low coefficient of friction, making them suitable for high-speed, high-temperature and high-precision application scenarios. Plastic materials are typically used in light-duty applications, while ceramic materials are suitable for extreme environments.
Accuracy class and tolerance class
Bearing precision refers to the size of the processing error in bearing manufacturing and is an important indicator of bearing performance. It reflects the degree of accuracy of the bearing in terms of geometry, size, rotational accuracy and so on. According to ISO standards, bearing accuracy can be divided into grade and tolerance systems.
Bearing tolerance refers to the bearing manufacturing size and design size of the difference between the range, which allows the bearing size, shape and position within a certain range of change. The tolerance size directly affects the rotational accuracy, load-carrying capacity and bearing service life. Bearing tolerance is usually divided into positive tolerance and negative tolerance; positive tolerance refers to the bearing manufacturing size being larger than the design size of the deviation, and negative tolerance refers to the manufacturing size being smaller than the design size of the deviation.

Explanation of different accuracy classes
- ISO accuracy classes (P0, P6, P5, P4, P2)
ISO accuracy classes (P0, P6, P5, P4, P2) are accuracy classification standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for bearings and other rotating machinery components. These grades reflect the degree of accuracy of bearings in terms of geometry, dimensions, rotational accuracy, etc., and are, in descending order, P0, P6, P5, P4, P2.
- ABEC rating system
The ABEC rating system is a set of standards developed by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA) under the Association/Committee for Annular Bearing Engineering (ABEC) for evaluating bearing tolerance classes. This system is primarily geared toward precision bearings, including deep groove ball bearings. It differentiates between different accuracy classes using numerical numbers (1 to 9), with higher numbers indicating higher bearing accuracy.
- Comparison between ISO and ABEC systems
Both the ISO and ABEC systems are valid standards for evaluating the accuracy of bearings. Still, they differ regarding the organization that developed them, their application’s scope, their grades’ classification, and how they are numbered. Designated organization: The International Organization for Standardization formulated the ISO system, and the American Bearing Manufacturers Association formulated the ABEC system. I. Scope of application: ISO accuracy grades are widely used for various rolling bearings. Although initially designed for skateboard shoe bearings, the ABEC system has gradually been applied to evaluate other precision bearings, especially in the U.S. market. Second, the grade division and numbering method: ISO system, ISO precision grade is usually expressed in P level, such as P0, P6, P5, P4, P2, etc. The smaller the number, the narrower the tolerance band and the higher the precision. Third, the ABEC rating system uses digital numbering to indicate the accuracy level; the larger the number, the narrower the tolerance band, and the higher the accuracy. The opposite of the ISO system of numbering. Fourth, the accuracy characteristics: ISO system, ISO accuracy grade from P0 to P2 gradually improve, each grade corresponds to a certain tolerance band range. The ABEC rating system from ABEC-1 to ABEC-9 progressively improves the accuracy requirements.
Impact on performance and applications
- Running accuracy
Running accuracy refers to the stability and accuracy of bearings in rotary motion; it is affected by the joint influence of precision and tolerance; high precision and small tolerance bearings can ensure higher running accuracy.
- Noise and vibration levels
High-precision bearings usually have lower noise levels and can maintain lower vibration levels during operation. When the tolerance is too large, the precision of the fit between the rolling elements, inner and outer rings and other parts of the bearing is reduced, which can easily lead to uneven clearance and shock vibration, thus increasing the noise; too large or too small a tolerance may lead to unstable vibration of the bearing during operation.
- Heat generation
High-precision bearings usually require smaller tolerance ranges to ensure the stability of their performance; tolerances that are too small may increase the difficulty and cost of manufacturing or lead to excessive assembly stress and accelerate bearing wear and damage. Therefore, when selecting precision and tolerance, they must be considered to balance the bearing’s performance, cost, and service life, among other factors.
- Bearing life
High-precision bearings and proper tolerance ranges can extend bearing life.
Deep groove ball bearing applications
Deep groove ball bearings are characterized by simple structure, high speed, and small coefficient of friction, and can withstand radial load or radial and axial simultaneously. The role of joint load in the industrial field is mainly used in the automotive and power industries.
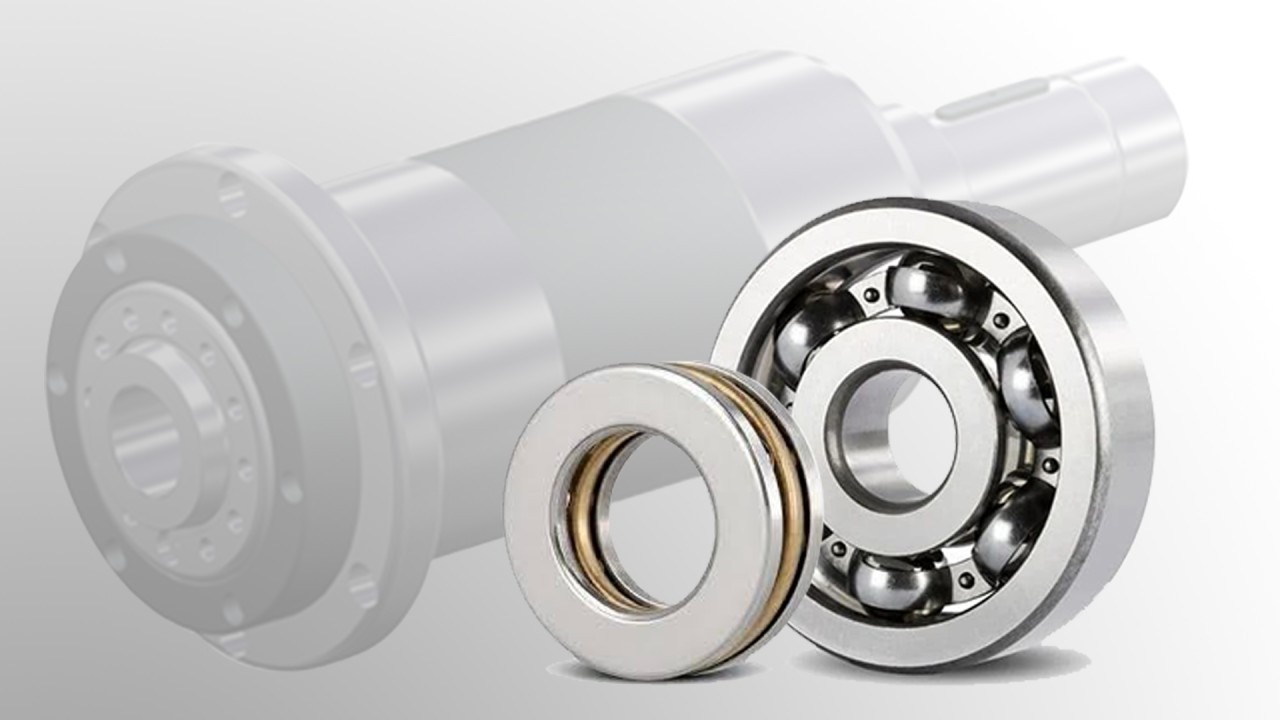

Common Uses in Vehicles
Deep groove ball bearings in the automobile industry are commonly used in automobile and motorcycle wheel bearings, transmission bearings, and other parts. They are used to bear the vehicle’s weight and the force of various road conditions to ensure the smooth running of the car. In the automobile, the engine, transmission, and other key components, at the same time, can provide normal operation and transmission to improve the car’s overall performance. Deep groove ball bearings in motors and generators can support not only rotating parts, reduce friction loss, and withstand load capacity but also have high precision, heat, high-speed resistance, easy installation and maintenance, etc. These advantages make them one of the indispensable key components in motors and generators. As a key component in heavy machinery, deep groove ball bearings can support rotating parts, reduce friction and wear, withstand heavy loads and high rotational speeds, improve the precision and reliability of machinery, and adapt to harsh working environments.
Specific requirements and challenges
- Size limitations: Deep groove ball bearings have limited mounting space, and their size selection is usually determined by mechanical design or design constraints. The main dimension table of the bearings is compiled according to the international scale bore size, so special attention needs to be paid to matching and selecting dimensions in practical applications.
- Speed and lubrication: The speed of deep groove ball bearings depends on factors such as their type, size, accuracy, type of cage, load, lubrication method and cooling method. The choice of lubrication method has an important influence on the speed and life of the bearing; usually, deep groove ball bearings are suitable for high-speed running occasions.
- Dimensional tolerances and rotational accuracy: The dimensional accuracy and rotational accuracy of deep groove ball bearings are according to ISO and JIS standards. For machinery requiring high precision and high-speed operation, it is recommended to use bearings with grade 5 or higher accuracy.
- Axial load: Deep groove ball bearings have certain limitations when bearing axial load. Usually, deep groove ball bearings can also withstand a certain amount of axial load after bearing a certain radial load, but the axial load is too large may shorten the service life of the bearings.
Deep groove ball bearing maintenance and troubleshooting
Deep groove ball bearings daily maintenance techniques can effectively maintain the performance and life of deep groove ball bearings mainly through regular inspection, cleaning and maintenance, selecting the right lubricant, adding the right amount of lubricant and paying attention to avoiding overload, shock and vibration.
Deep groove ball bearings can effectively reduce the failure rate of deep groove ball bearings by formulating a maintenance plan, including determining the maintenance cycle, specifying the maintenance content (cleaning, lubrication, inspection, recording), etc.; adopting condition monitoring technology, including vibration monitoring, temperature detection, sound detection, etc.; and implementing predictive maintenance methodology, including the collection of inspection data and the establishment of a life prediction model for bearings, and other methods.
Common failures of deep groove ball bearings include fatigue spalling, wear, rust, and cage damage. The noise and vibration problem can be solved by choosing bearings with high precision grade and low noise characteristics, adopting the correct lubrication method, etc. The causes of overheating of deep groove ball bearings include poor lubrication, seizing inner and outer rings, incorrect mounting, etc. They can be solved by timely refuelling or replacing lubricants, timely cleaning or replacing bearings and reasonably designing bearing loads.

Deep groove ball bearing mounting guide
Bearing mounting should be based on the bearing structure, size and bearing parts with the nature of the determination; the pressure should be added directly to the tightly fitted to the end of the ring surface and shall not be through the rolling body to pass the pressure. Installation methods mainly include press fit, heating fit and cold installation. Installation should pay attention to keeping clean, avoiding violent installation, choosing the right tool and so on.
Installation
Cold press installation method:
The deep groove ball bearing cold pressure mounting method can be understood as in the bearing or mating parts after cooling treatment, the use of pressure will be mounted in place of the process; this method is suitable for small and medium-sized deep groove ball bearings, when the bearing and the shaft or the bearing housing of the fit between the tighter, the use of cold pressure mounting method can reduce the difficulty of mounting, at the same time should pay attention to the need for strict control of the cooling temperature and time, in order to avoid the bearings to cause unnecessary damage.
Heat installation method:
The hot mounting method for deep groove ball bearings is suitable for bearings with larger dimensions or larger overload. The main steps are heating the bearing, rapid mounting, cooling and fastening. Attention should be paid to controlling the heating temperature during the mounting process, protecting the bearings during the mounting process, and checking whether the bearings are mounted in place after the mounting is completed.
Maintenance and care suggestions
- Selection of suitable lubricant: Choose a suitable lubricant or grease according to the bearing’s environment and operating conditions, and check and replace the lubricant regularly.
- Bearing cleaning: Bearings are susceptible to dust, moisture and other pollutants in the working environment, which can accelerate wear and corrosion and reduce their lifespan. Bearings should be cleaned with appropriate detergents and tools and then wiped dry with a clean cotton cloth or paper towel.
- Avoid overloading: Check the bearings’ operation regularly to ensure that they are operating within the rated load. If any abnormal vibration, noise or temperature rise is found in the bearings, they should be stopped, inspected and dealt with in time.
- Reasonable storage: The bearings should be cleaned and lubricated before storage and protected with a rust inhibitor. They should be stored in a dry, clean and non-corrosive gas environment, avoiding direct sunlight and high temperatures. Regularly check the storage conditions and status of the bearings to ensure they are in good condition.
How to choose a deep groove ball bearing manufacturer
There are many bearing manufacturers worldwide, and to choose the right deep groove ball supplier, you need to compare and select carefully. The following list some of the world’s more well-known bearing manufacturers.
Criteria for evaluating bearing manufacturers
- Product quality and precision
Product quality and precision are key factors for evaluating deep groove ball-bearing manufacturers. Product quality mainly includes raw material quality, manufacturing process, quality control system and product certification and standards; precision mainly includes dimensional, rotational, and accuracy levels. By examining product quality and precision, we can specifically understand deep groove ball manufacturers’ production capacity and product quality level.
- Technological innovation and R&D capabilities
Technological innovation and R&D capability are the key factors for assessing deep groove ball-bearing manufacturers. Technological innovation includes applying new materials, manufacturing process innovation, lubrication and sealing technology, etc.; R&D capability includes the R&D team and investment, R&D results and patents, customized R&D capabilities and industry-university-research cooperation. Through the assessment of technological innovation and R&D capability, the strength level of deep groove ball manufacturers can be fully understood.
- Industry reputation and customer reviews
Industry reputation and customer evaluation are key to evaluating deep groove ball-bearing manufacturers. By assessing these two factors, it is possible to get a comprehensive picture of the manufacturer’s market position, product quality, service level and customer satisfaction.
Top brands and their specialities
- SKF: SKF Group is a leading global supplier of a wide range of bearing products, including deep groove ball bearings, which are widely used in many industrial fields and also occupy an important position in the deep groove ball-bearing market.
- Germany FAG/INA: FAG/INA, part of the Schaeffler Group, is a global leader in the production of rolling bearings and linear motion products with industry-leading quality and performance.
- NSK: NSK is Japan’s earlier design and production of bearings manufacturers; the company has now expanded to automotive parts, precision machinery products, electronic applications, and other fields and is the world’s leading bearing manufacturer.
- TIMKEN Timken: Founded in 1899 in the United States, TIMKEN Timken Company is the world’s leading supplier of high-quality anti-friction bearings, related products and services and alloy steel and steel components.
- NTN: NTN is one of the world’s comprehensive precision machinery manufacturers, founded in Japan. Its products are widely used in orbit satellites, aviation, railway and automobile, office equipment and food machinery and other industrial sectors in various fields. It has an important position in the deep groove ball bearing market; the quality of its products and technical level are at the forefront of the industry.
- KOYO bearings: KOYO bearings are the brand of Jettaigt (China) Investment Co., Ltd, which started in Japan in 1921. The company enjoys an important position in the field of bearings, automobile power driving and mechanical equipment.
- Wafangdian Bearing Group Co., Ltd (ZWZ Waxial): Wafangdian Bearing Group is the birthplace of China’s bearing industry; the company produces bearings for major technical equipment, rail transportation bearings, automotive bearings, military equipment bearings and other products.
- Harbin Bearing Manufacturing Co., Ltd (HRB) is a well-known bearing manufacturer in China. The company is mainly engaged in the production of railroad bus speeding bearings, precision machine tool spindle bearings, and mining metallurgy bearings.
- Renben Group Co., Ltd (C&U Renben) is one of the leading enterprises in China’s bearing industry; the company mainly produces bearings and, at the same time, is involved in commercial supermarkets, electromechanical trade and other sectors.
- TFL Bearing Co., Ltd: Located in Jinan City, Shandong Province, China, the company is a bearing-based, research and development, production and sales as one of the precision bearing manufacturing enterprises to provide various customers with bearing products, covering a variety of industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do single-row deep groove ball bearings differ from double-row bearings?
- Single-row deep groove ball bearings: These kinds of bearings only have deep grooves on one side of the rolling body and cage. The structure is relatively simple. This design makes single-row ball bearings have low friction and heat generation in high-speed operation, making them suitable for low-load and high-speed operation occasions. However, its bearing capacity is relatively weak and unsuitable for large radial loads.
- Double-row deep groove ball bearings: These bearings have deep grooves and rolling elements on both sides, which complicate the structure. Therefore, double-row ball bearings can withstand higher radial loads and are suitable for low—or medium-speed operation and high-load occasions. However, they may produce higher friction and heat generation at high-speed operation.
2. Is the durability of miniature bearings comparable to that of standard-sized bearings?
Miniature bearings are designed and manufactured with special applications in mind, so their durability can be comparable to that of standard-sized bearings when properly used and maintained. However, due to size constraints, they may be more susceptible to overloading or contamination and, therefore, may require more frequent inspection and maintenance in some applications.
3. What are the advantages of deep groove ball bearings in high-speed applications?
The advantages of deep groove ball bearings in high-speed applications are mainly due to their design construction to withstand radial and axial loads, low friction, and low resistance to motion. Deep groove ball bearings also offer durability and low maintenance requirements for high-speed operation.
4. What are common mistakes when installing deep groove ball bearings?
I. Improper installation method; II. Too tight or too loose fit; III. Damage caused by knocking installation; IV. Improper heating installation; V. Improper lubrication; VI. Improper storage and custody; VII. Wrong installation sequence and steps.
5. How do I choose the right accuracy class for my deep groove ball-bearing application?
Selecting the correct accuracy class requires comprehensive consideration of a number of factors, mainly including clarifying the requirements for use and the working environment, understanding the meaning of the accuracy class, selecting the appropriate accuracy class according to the needs, considering the economic benefits, and referring to professional advice.
