Insulated Bearings Designator
Introduction
Bearing code refers to a set of symbols used to indicate the inner diameter of the bearing, diameter series, width series and type. Code usually consists of letters and numbers, up to five digits, divided into the basic, rear, and front codes. The main difference between the insulated bearings designation and the common bearing designation is that the insulated bearings designation will add some suffixes, which are used to indicate the insulation characteristics of the bearing.
Components of rolling bearings
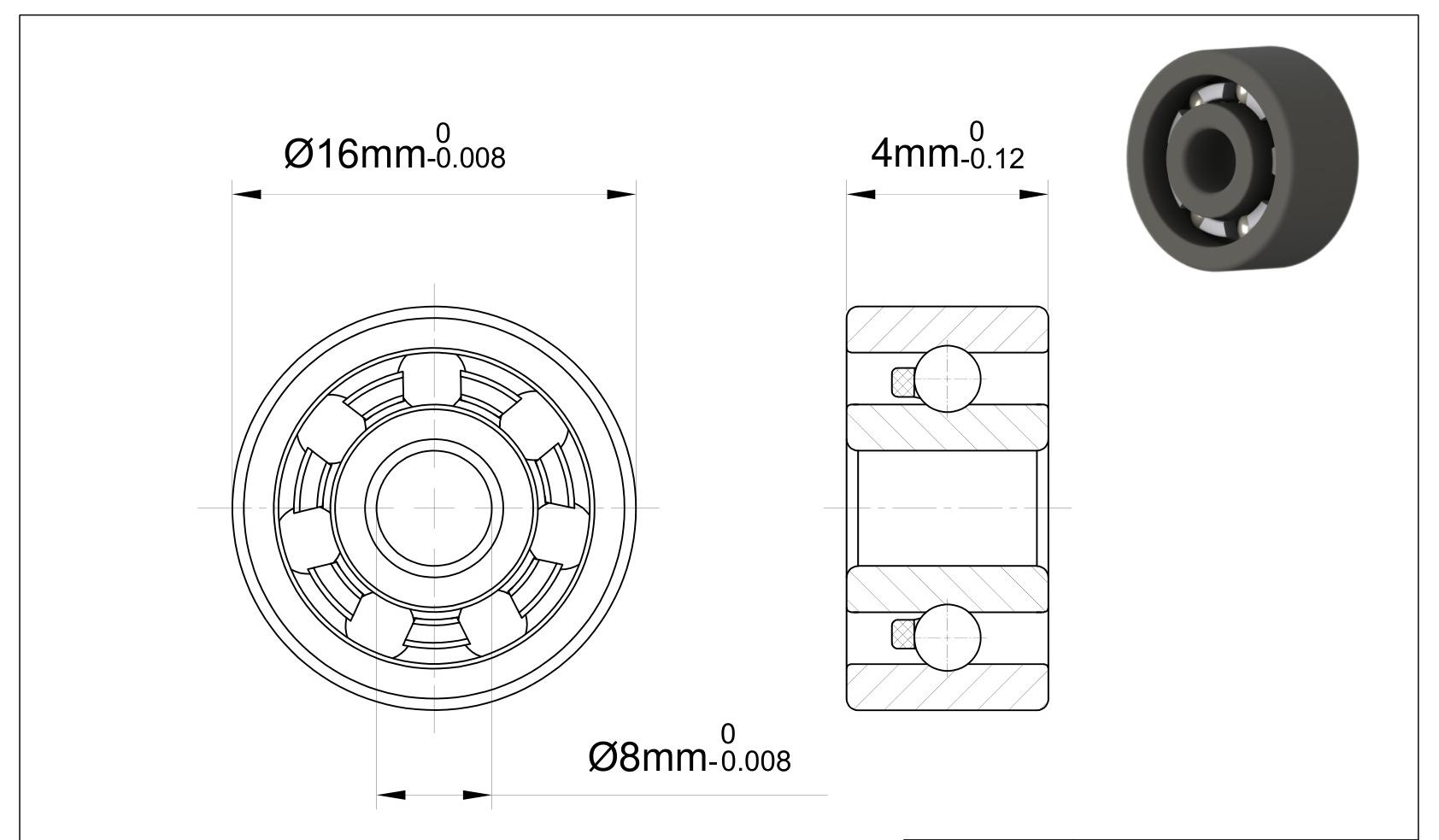
Rolling bearings are mainly composed of four parts: inner ring, outer ring, rolling element, and cage. The inner ring is usually closely matched with the shaft and rotates with the shaft. The outer ring is usually matched with the holes of the bearing housing or mechanical parts and plays a supporting role. The rolling element is the core component of the bearing, which rolls between the inner ring and outer ring to reduce friction. The cage is used to evenly separate the rolling elements to prevent them from colliding with each other and to ensure the normal movement of the rolling elements.
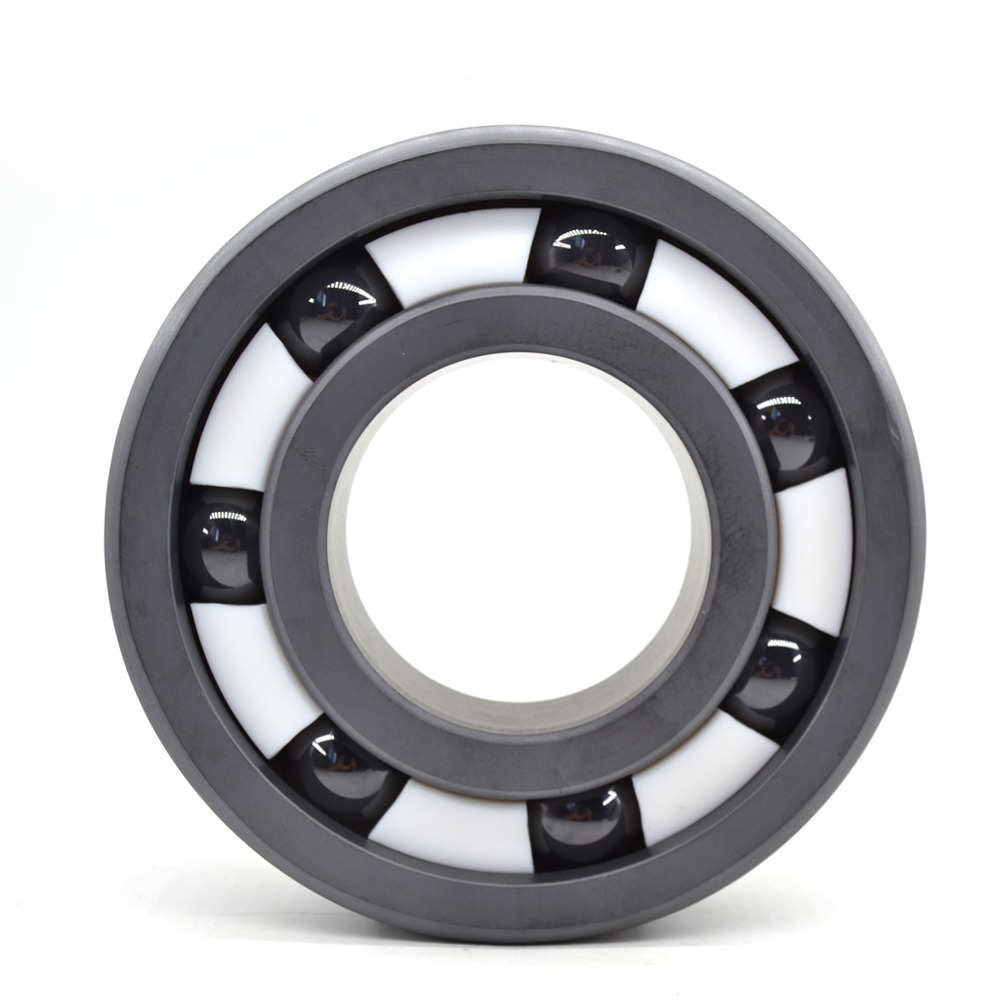

Rolling bearing four big pieces of code
| Number | Component | Nicknames |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | outer ring | 1 |
| 2 | inner ring | 2 |
| 3 | rolling element | 4 |
| 4 | cage | 07/46 |
Front code
| Nicknames | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| L | Separable inner or outer rings for separable bearings | LNU205 |
| R | Bearings without separable inner and outer rings (needle roller bearings only for NA type) | RNU205 |
| K | Roller and cage assemblies | K81105 |
| WS | Axial cylindrical roller-bearing rings | WS81105 |
| GS | Thrust cylindrical roller bearing housings | GS81105 |
| F | Radial ball bearings with flanged outer ring (only for d≤10mm) | F619/5 |
| KOW | Thrust bearings without shaft collar | KOW-51105 |
| KIW | Thrust bearings without seat | KIW-51106 |
| LR | Bearings with separable inner or outer rings and rolling element assemblies | —— |
Rolling bearing designation
The basic code of the bearing is based on the bearing type code, size series code, and the inner diameter code of the three parts of the left to right order.
Type code
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double Row Angular Contact Bearings | Self-aligning ball bearings | Spherical roller bearings and thrust spherical roller bearings | Tapered roller bearings | Double-row deep groove ball bearings | Thrust ball bearings |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | N | U | QJ |
| Deep groove ball bearings | Angular contact ball bearings | Thrust cylindrical roller bearings | Cylindrical roller bearings | Spherical Ball Bearings | Four-point contact ball bearings |
Size Series Designator
The size series code is calculated by the bearing width (height), degree series code (a number), and diameter series code (a number) for the composition of the left and right arrangement. It reflects the same kind of bearing in the ring aperture diameter of the same inner and outer ring width thickness of the different and different sizes of the rolling element. Obviously, the size series code of different bearings with different outer dimensions and bearing capacities is different. Size series code can sometimes be omitted: in addition to tapered roller bearings, the rest of the various types of bearings width series code “0”; are omitted; deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings 10 size series code in the “1” can be omitted; double-row deep groove ball bearings Width series code “2” can be omitted.
I.D. Code
| Nominal bearing bore d [mm] | I.D. Code | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0.6~10 non-integer | Directly expressed in nominal inside diameter in millimetres, separated from the size series designation by a "/." | 618/2.5 d=2.5mm |
| 1~9 integers | Nominal inner diameter in millimetres directly expressed, for deep groove and angular contact ball bearings 7, 8, 9 diameter series, the inner diameter and size of the series code before the use of "/" Separation | 625、618/5 All d=5mm |
| 10~17(10,12,15,17) | 00,01,02,03 | 6203 d=17mm |
| 20~480 not including 22、28、32 | The quotient of the nominal inside diameter is divided by 5, and the quotient is a single digit. You need to add a zero in front of the quotient, such as 08 | NU307、 d=35mm 63/22、 d=22mm |
| ≥500及22、28、32 | Expressed directly in nominal inside diameter in millimetres, but separated from the size series by a "/." | Spherical roller bearings: 230/500 d=500mm |
Rear Code
The posterior code indicates the structure of the bearing, cage, sealing and dustproof, tolerance, clearance and other technical requirements, which are located after the basic code.

Internal structure code
| Number | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A、B、C、D、E | 1) Indicates internal structural changes 2) Indicates a standard design, the meaning of which varies with different types and structures. | B 1, Angular contact ball bearings Nominal contact angle a = 40° 7205B 2、Tapered roller bearings with increased contact angle 32305B C 1, Angular contact ball bearings Nominal contact angle a = 15° 7005C E 1, Reinforced NU 207 E |
| AC D ZW | Angular contact ball bearings Nominal contact angle a=25° Split Bearing Needle roller cage assembly Double-row | 7210 AC K 50×55×20 D K 50×55×20 ZW |
Seals, Dust Covers, and External Shape Change Designators
| Number | Meaning | Number | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| RZ | Single-sided with skeleton-type rubber seal (non-contact) | 2RZ | Double-sided with skeleton-type rubber seal (non-contact) |
| RS | Single-Sided with Skeleton Rubber Seal (Contact) | 2RS | Double-sided with skeleton-type rubber seal (contact type) |
| Z | Single-sided dust cover | 2Z | Double-sided dust cover |
| N | Stop the groove on the outer ring | NR | Outer ring with stop groove and stop ring |
| K | Bearings with tapered bore, taper 1:12 | K30 | Bearings with tapered bore, taper 1:30 |
Cage structure, material designation
| Number | Meaning | Number | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cage materials | Cage structure type and surface heat treatment | ||
| F | Solid cage in steel, ductile iron or powder metallurgy | H | Self-locking pocket hole cage |
| Q | Bronze Solid Cage | W | Welding Cage |
| M | Solid brass cage | R | Riveted Cage |
| L | Light alloy solid cage | D | Carbonitriding cage |
| T | Phenolic Laminated Fabric Tube Solid Cage | C | Plated cage |
| TN | Engineering Plastic Molded Cage | A | outer ring guide |
| J | Steel Plate Punching Cage | B | Inner Circle Guidance |
| V | Fully loaded rolling element (no cage) | S | Lubrication grooves on guide surfaces |
Tolerance Class Designator
| Code reference | Sample comparison | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| new standard | old standard | new standard | old standard |
| P0 | G | 6203 | 203 |
| P2 | B | 6203/P2 | B203 |
| P4 | C | 6203/P4 | C203 |
| P5 | D | 6203/P5 | D203 |
| P6 | E | 6203/P6 | E203 |
| P6X | EX | 30210/P6X | Ex7210 |
Gap code
The bearing clearance code is used to indicate the size of the clearance between the rolling element and the inner and outer rings inside the bearing. The size of the clearance has an important effect on the bearing’s fatigue life, vibration, noise temperature rise and other properties. The clearance code includes Cm, C0, C1, C2, C3, C4 and C5, which:
C0: standard clearance; this code is generally omitted in the bearing type without marking.
C1: Swimming gap by the standard provisions of 1 group, less than 2 groups.
C2: Swimming gap following the standard provisions of the 2 groups, less than 0 groups.
C3: Swimming gap per the standard specified in the group of 3, greater than 0 groups.
C4: Swimming gaps conform to the standard for groups of 4, greater than 3.
C5: Swimming gaps are under the standard for groups of 5, greater than 4.
In descending order: C1<C2<Cm<C0<C3<C4<C5
Other codes

Vibration code
Bearing vibration code is mainly divided into acceleration type and speed type two, respectively, with different units of measurement and code.
Acceleration type vibration designator:
Z1, Z2, Z3: These codes indicate different levels of vibration, of which Z1 level applies to the bearing vibration of general requirements of the finished bearing inspection, Z2 level applies to the Y series of motors and the corresponding requirements of other motor bearings, Z3 level applies to the vibration of the strict requirements of the situation.
Velocity-type vibration designator:
V, V1, V2, V3: These codes indicate different levels of vibration, of which level V is suitable for bearing manufacturers for the standard range of deep groove ball bearing vibration inspection, level V1 is ideal for bearing vibration has general requirements for bearing finished product inspection, level V2 is ideal for the Y series of motors and the corresponding requirements of other motor bearings, level V3 is suitable for vibration of the strict requirements of the situation.
Configuration code
DB: Pairwise back-to-back installation
DF: Pair face-to-face installation
DT: Installed in pairs in series
Example of Bearings Designation
| Base code | Rear Code | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||
| Example | Type code | Size Series Designator | I.D. Code | Internal composition | Sealing structure | Cages and theirm materials | Bearing Materials | Tolerance level | Clearance |
| 6204-2Z/P63 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 2Z | P6 | C3 | |||
| NUP207E | NUP | 2 | 7 | E | |||||
| 51840/P52 | 5 | 18 | 40 | P5 | C2 | ||||
Insulated Bearings Suffix Code
Suffix codes for insulated bearings are used to identify the insulation characteristics and other additional characteristics of the bearing. These suffix codes may vary depending on the manufacturer and type of bearing but usually follow certain naming rules. The following are some common insulated bearings suffix codes and their meanings:

SKF Insulated Bearings
VL0241: Standard outer ring coating, 3000V protection, minimum 200MΩ resistance. As: 6316/C3VL0241
VL2071: Standard inner ring coating, 3000V protection, minimum 200MΩ resistance. As:6326 M/C3VL2071
VL0246: Advanced outer ring coating, 3000V protection, minimum 400MΩ resistance.
VL2076: Advanced Inner Ring Coating, 3000V Protection, Minimum 400MΩ Resistance. As: 6332M.C3.VL2076
HC: Ceramic (Silicon Nitride) rollers for maximum insulation properties. As:6316/HC5C3S0.
FAG Insulated Bearings
J20AA: Coated outer ring, 3000V protection, suitable for dry and humid environments. As:6330-M-J20AA-C3
J20C: Inner ring coated, 3000V protection, suitable for dry and humid environments. As:6336-M-J20C-C4
J20AB: Coated outer ring, 1000V protection, especially suitable for humid environments. As:6228-J20AB
J20B: Simple protection, 500V protection, for dry environments. 6213-J20B-C4
J20A: Special protection for large-size bearings, 1000V protection for dry environments. As: NU1030M1-C4-J20A
HC: Ceramic (Silicon Nitride) rollers for maximum insulation performance. As: HC6002-2Z
NTN Insulated Bearings
7MC: standard ceramic coating, 5kV protection. As:7MC-6311M2C3
7MC2: Protective ceramic coating, 3kV protection. As:2TS2-7MC2-NH318E
7MC3: Standard ceramic coating, 3kV protection. As:7MC3-6314C3
7MP: Standard resin (PPS) coating, 5kV protection. As:2TS2-7MP-NU214
7MP2: Heat dissipation, anti-creep type resin (PPS) coating, and 5kV protection. As:7MP2-6312
CN03: Use of silicon nitride ceramic rollers.
NKE Insulated Bearings
SQ77: Coated outer ring, guaranteed at least 1000V AC or DC breakdown resistance. As:NU315-E-M6-C3-SQ77
SQ77E: Coated inner ring, guaranteed at least 1000V AC or DC breakdown resistance. As:6328-M-C3-SQ77E
-HYB: Ceramic (silicon nitride) rollers for maximum insulation performance. As:6330-C3-HYB
NSK Insulated Bearings
SN24: ceramic (silicon nitride) balls for small and medium-sized deep groove ball bearings. As:7018 A5-SN24-TR-DUDL-P3
HDY2: outer ring ceramic coating for medium and large deep groove ball bearings, insulation resistance of 10,000MΩ or more, insulation breaking voltage DC6000V or more. As:6220-HDY2-C3
Conclusion
The designation of insulated bearings adopts international bearing designations, such as outer ring insulated bearing designation VL0241, inner ring insulated bearing designation VL2071, etc. This standardization makes insulated bearings highly interchangeable in the market. It can be completely replaced with ordinary bearings, which are convenient for users to choose and use flexibly in different equipment and projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is an insulated bearing designator?
The design symbols for insulated bearings consist mainly of international bearing designations and specific suffixes. The design symbols for insulated bearings are usually international bearing designations followed by a specific suffix to identify their insulating characteristics.
- How can I interpret bearing designators correctly?
To interpret bearing design symbols correctly, one must understand the basic structure and meaning of the code. Bearing code usually consists of the basic code before and after the code. The basic code indicates the bearing’s basic type, structure and size; the front code indicates the bearing’s structural shape, size, tolerance and technical requirements. The rear code indicates the internal structure, sealing, clearance precision and other auxiliary information.
- What are the benefits of using designators for bearing selection?
The main benefits of using design symbols for bearing selection include increased design accuracy and efficiency, reduced errors, and ease of communication and exchange. In addition, using design symbols can help engineers better understand the principles and methods of bearing design.
- Are TFL insulated bearings compatible with other brands?
Generally, our bearings are compatible with international standards. The compatibility of TFL insulated bearings needs to be specifically analyzed to see if their models and specifications are consistent with other brands of bearings and to consider the working environment and installation requirements. It is recommended that the replacement bearings be chosen carefully to ensure that they meet the use requirements.
- How do I contact TFL for more information?
To learn more about TFL Insulated Bearings, you can find us by calling or sending an e-mail, visiting our official website or contacting Alibaba. Below:
Call Us: 0086 15806631151
Email Us: info@tflbearing.com / candice004@foxmail.com
