Understanding and Preventing Bearing Rust: A Simple Guide
Introduction
Bearings are crucial parts of machines, but they can fail due to a sneaky problem: rust. Rust isn’t just a surface issue—it can wreck a bearing’s performance and lifespan.
In this guide, we’ll break down what bearing rust is, how to spot it, and most importantly, how to stop it. Ready to learn how to keep your bearings rust-free? Let’s get started!
What Is Bearing Rust and Why Is It a Big Deal?
Rust is a type of corrosion that happens when bearings made of steel react with moisture in the air. It’s a chemical change that can cause serious damage:
-
Inside the bearing: When rust forms on the rolling surfaces (where the bearing moves), it creates noise and vibrations. This can lead to a vicious cycle where the rust spreads, ruining lubrication and damaging the bearing even more.
-
Outside the bearing: Rust on the outer parts can weaken the bearing’s structure, potentially causing it to crack or break under pressure.
-
Quick Question: Ever wondered why some bearings seem to break down faster than others? Rust might be the hidden culprit!

How to Spot Bearing Rust: Diagnosis Tips
Rust usually shows up in two scenarios:
- When the bearing isn’t moving: Rust often forms on the parts that aren’t in motion or during long periods when the machine is off.
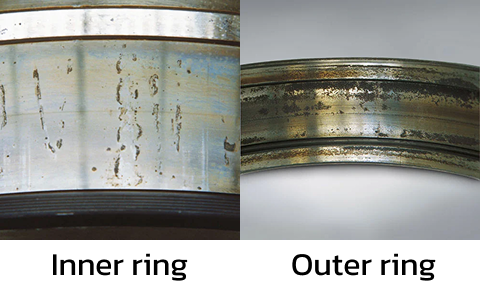
- On non-moving surfaces: Even when the bearing is running, rust can sneak onto surfaces that don’t move, like the outer rings.
Here’s a simple way to tell when rust happened:
-
Rust on the rolling path with evenly spaced marks (matching the spacing of the rolling elements): This likely happened when the bearing was stopped. It could be from before installation or during downtime after installation.
-
Rust on the outer or inner rings: These areas are usually protected by fittings, so rust here might mean something’s wrong with the setup or environment.
-
Pro Tip: If you see rust on a bearing, think about when it might have formed. Was the bearing sitting idle for too long? Or is the environment too damp?
Common Causes of Bearing Rust
-
Storage issues: Bearings can rust if stored in humid places or if their protective packaging is damaged.
-
Condensation: Temperature changes can cause moisture to form inside the bearing, especially if it’s moved from a cold to a warm area.
-
Poor lubrication: Grease usually protects bearings from rust, but if it’s not applied properly or if water gets into the grease, rust can form.
-
Wet working conditions: If the machine operates in a damp environment, rust is more likely, especially if seals aren’t doing their job.
How to Prevent Bearing Rust: Practical Steps
Stopping rust is all about keeping moisture away from the bearing. Here’s how you can do it:
Store Bearings Properly
-
Humidity control: Keep storage areas dry. Check with the bearing manufacturer for recommended humidity levels.
-
Keep packaging intact: Don’t open the bearing’s packaging until you’re ready to use it. If the packaging is damaged, cover it to block moisture.
-
Did You Know? Most bearings come with rust-preventive oil. You usually don’t need to wash it off—just add grease and go!
Handle Bearings Carefully
-
Avoid condensation: When moving bearings from cold to warm areas, give them time to adjust to prevent moisture buildup.
-
Don’t freeze without care: Some factories freeze bearings for installation. If you do this, make sure to prevent condensation inside the bearing—it’s tricky to clean!
Use the Right Lubrication
-
Grease is your friend: Most greases have anti-rust ingredients and block oxygen from reaching the steel.
-
Check for water: If the grease looks watery, it might not protect the bearing anymore. Replace it if needed.
Seal It Up
-
Choose the right seals: If your machine works in wet or steamy conditions, use seals designed to keep moisture out.
-
Inspect regularly: Make sure seals are in good shape and replace them if they’re worn out.
Final Thoughts: Bearing Rust Is Sneaky, But You Can Beat It
Bearing rust might seem like a small issue, but it can lead to big problems if ignored.
The good news? With a few simple steps—like proper storage, careful handling, and good lubrication—you can keep your bearings running smoothly for longer.

