Cylindrical Roller Bearing: What Is It?
Quick Guide: Types of Cylindrical Roller Bearings (N, NU, NJ, NUP)
The main difference between cylindrical roller bearing types lies in the arrangement of the flanges (ribs) on the inner and outer rings. This structure determines whether the bearing can carry axial loads (thrust) in addition to radial loads.
-
NU Series (No Inner Ribs):
Features double ribs on the outer ring and no ribs on the inner ring. The inner ring can be removed, allowing for easy mounting and dismounting. Ideal for carrying heavy radial loads where thermal expansion of the shaft is expected (non-locating bearing). -
N Series (No Outer Ribs):
Features double ribs on the inner ring and no ribs on the outer ring. Like the NU series, it permits axial displacement between the shaft and housing, making it a perfect floating bearing choice. -
NJ Series (Single Direction Axial Load):
Has double ribs on the outer ring and a single rib on the inner ring. This design allows the bearing to support heavy radial loads and carry axial loads in one direction, guiding the shaft axially. -
NUP Series (Locating Bearing):
Features double ribs on the outer ring, one fixed rib on the inner ring, and a separate loose rib washer. This allows the bearing to carry axial loads in both directions, functioning as a locating bearing to fix the shaft position.
| Series Type | Configuration (Ribs) | Axial Load Capacity | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| NU Series | 2 Outer / 0 Inner | None (Allows expansion) | Floating bearing end |
| N Series | 0 Outer / 2 Inner | None (Allows expansion) | Floating bearing end |
| NJ Series | 2 Outer / 1 Inner | One Direction | Shaft guidance (1-way) |
| NUP Series | 2 Outer / 1 Inner + Ring | Both Directions | Locating bearing (Fixed) |
The N, NU, and NJ series have critical differences in installation and axial load handling. If you are selecting a bearing for a specific motor or gearbox, check out our detailed engineering guide: 【Difference Between N, NU, NJ & NUP Series】
Cylindrical Roller Bearing: What Is It?
Defining Cylindrical Roller Bearings and How They Work
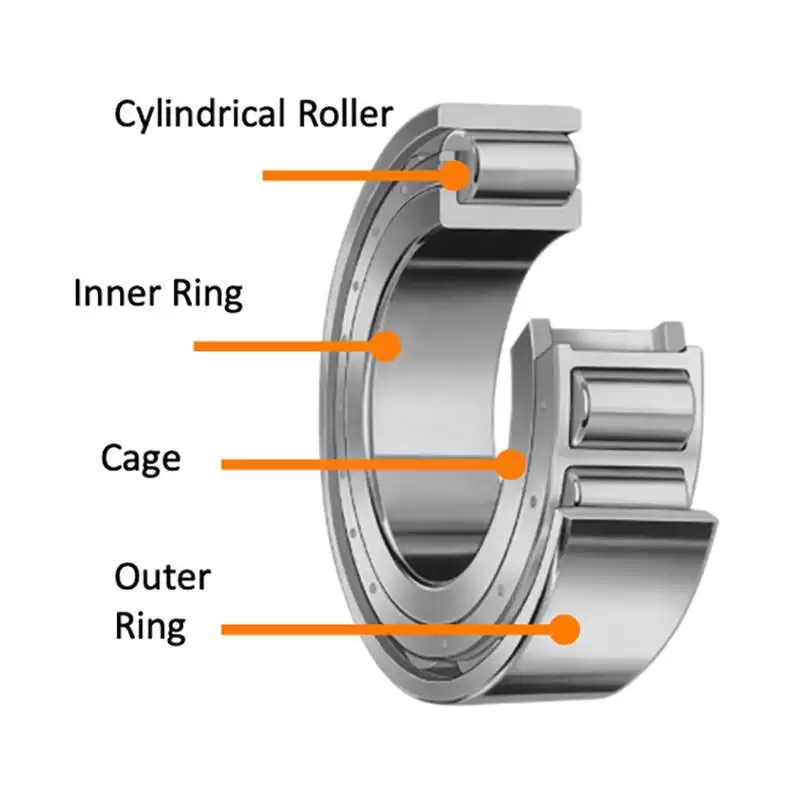
Differences from other types of bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings are superior to ball bearings at managing heavy loads and high-speed operations, which makes them perfect for heavy-duty equipment. Ball bearings, on the other hand, work well under light loads and when exact placement is needed. The needle roller bearing is another significant member of the roller bearing family. The rollers in these bearings resemble needles and have a smaller diameter than cylindrical rollers. They are ideal for usage in small areas due to their low cross-sectional height, which helps to make machinery lighter and more compact. Tapered roller bearings are the recommended option for applications requiring the simultaneous handling of axial and radial loads. Conical rollers, which are used in these bearings, effectively control both axial and radial loads in a single direction. Spherical roller bearings are the best at handling misalignment and large loads. These bearings, which include barrel-shaped rollers, enable the cage, rolling elements, and inner ring to rotate at an angle to the outer ring. Because of this feature, spherical roller bearings are essential for machines that are subject to shaft deflection or heavy loads.
How Do Cylindrical Roller Bearings Operate?
Interaction Between Racetracks and Rollers
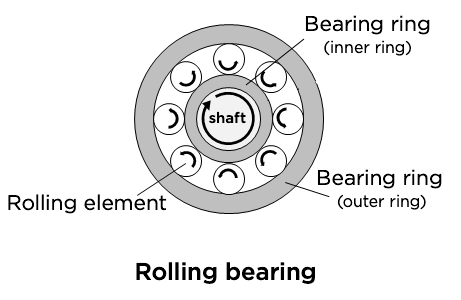
Roles of the Inner and Outer Rings
Design Principles for Efficient Support
Cylindrical Roller Bearings’ Advantages
Cylindrical roller bearings are real workhorses in the world of machinery. They stand out because of their ability to handle heavy loads, their durability, and their adaptability across different industries. Let’s break down their key advantages into an easy-to-read table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Load Capacity | Thanks to their line contact design, cylindrical rollers can handle large radial loads with ease. This makes them perfect for heavy machinery like gearboxes, wind turbines, and pressure-intensive applications. |
| Sturdiness and Lifespan | The line contact distributes radial loads evenly, reducing stress and fatigue damage. This ensures better durability and longer lifespan compared to point contact designs. |
| Versatile Applications | Whether it’s electric motors, rail systems, or vehicle transmissions, cylindrical roller bearings excel. They can also handle heat, vibrations, and work well in both lubricated and dry conditions, making them incredibly adaptable. |
Applications of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings come in various types designed for specific applications. Whether it’s industrial machinery, automotive components, or heavy load equipment, the right bearing type ensures maximum performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed table that includes commonly used bearing types for each application:
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Industrial Machinery | Ideal for large or fast-spinning shafts in conveyor systems, pumps, and compressors. Commonly used types include NU and N designs for high-speed applications and NJ types for axial load support in energy, paper, and steel industries. |
| Automotive Components | Found in wheel axles and differentials, ensuring smooth rotation and torque management. Frequently used models include NUP designs for axial positioning and RN series for compact designs that handle high stress. |
| Heavy Load Equipment | Essential for heavy-duty machines like cranes and mining equipment. NN and NNU series are often used due to their high radial load capacity and ability to handle impact and vibration in harsh environments like lifting systems. |
Cylindrical Roller Bearings’ Salient Characteristics
Extremely Accurate
Minimal Friction
Resistance to Temperature
Cylindrical Roller Bearing Cages: Brass vs. Steel vs. Polyamide
Selecting the right cage (separator) material is just as important as choosing the bearing type. The cage guides the rollers and determines the bearing’s suitability for speed, vibration, and temperature limits. Here are the three most common materials and their specific codes:
Pressed Steel (Suffix J)
This is the standard cage for most general-purpose applications. Pressed steel cages are lightweight and provide plenty of space for lubricant to circulate. They are cost-effective and suitable for normal operating temperatures and moderate speeds. However, they are less resistant to shock loads compared to brass.
Machined Brass (Suffix M/EM)
For heavy-duty applications, machined brass is the gold standard. Brass cages are exceptionally robust and can withstand high vibration, heavy acceleration, and shock loads that would destroy a steel cage. They are commonly found in large-sized bearings used in mining, crushing, and vibrating screens. While more expensive, they offer the highest reliability in harsh environments.
Polyamide / Nylon (Suffix TVP/ET)
Polyamide 66 (fiberglass reinforced) cages are becoming increasingly popular for small to medium-sized bearings. They are extremely lightweight, offering the lowest friction and quietest operation, making them ideal for high-speed motors. However, they have a temperature limit (usually up to 120°C/250°F). They should not be used in vacuum environments or with certain synthetic lubricants that can degrade the plastic.
