Let you quickly understand thrust bearings from 4 aspects
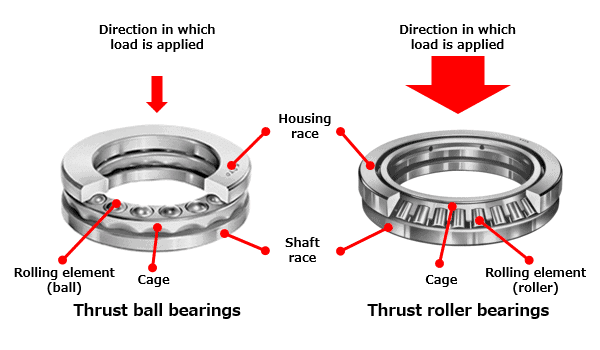
Thrust ball bearings are classified into those with flat seats or aligning seats depending on the shape of the outer ring seat (housing washer). They can sustain axial loads but no radial loads. For Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings, pressed steel cages and machined brass cages have usually been used. The cages in Double-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings are the same as those in Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings of the same diameter series. TFL can provide a full range of thrust ball bearings and thrust roller bearings.
- Available in two designs: single direction and double direction.
- To accommodate initial misalignments in an assembly both designs are available with spherical aligning seats or aligning seat washers.
- High-quality steel-ultra clean steel to extend bearing life by up to 80%.
- Advanced Grease Technology — TFL lubricants that can extend grease life and performance.
- High-Grade Balls — Quiet and smooth operation even at high speed.
- Optional seating rings take initial misalignment.
As a global leader in the bearing industry, TFL provides custom solutions to lead your industry. We find solutions to get the bearing you need and reduce your long lead times. Whether that is a bearing that is modified, manufactured, or repaired to your specification, we can help you. In this article, we discuss thrust bearings, from designs to applications and more.
Chapters
Chapter 1 What are Thrust Bearings, Types, and How Do They Work
Thrust bearings include a variety of bearings that assists axial loads or axial force. It is an axial bearing that permits rotation between parts. Thrust bearings support the axial thrust of both horizontal and vertical shafts.
The functions prevent the shaft from drifting in the axial direction and transfer thrust loads applied on the shaft.
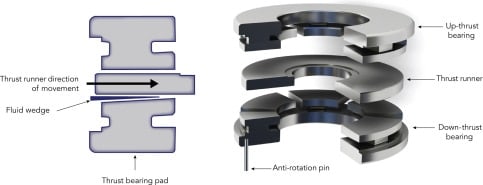
Thrust bearings are generally seated against a raised thrust collar around the shaft. The thrust collar allows the axial load to be transferred from the shaft to the bearing. Thrust bearings are typically used in pairs on each side of the thrust collar.
Depending on the usage or application, there are many types to choose from.
General types:
1. Flat land bearing – made of a single flat disc with grooves and no moving parts
2. Tilting pad bearing – consists of moveable metal plates called thrust shoes
Types of Thrust Bearings that Support Axial Load
Thrust bearings support a force applied in the same direction as the shaft. They can be categorized into two major types: Thrust ball bearing and Thrust roller bearing. The thrust ball bearings are used to deliver high performance, while the thrust roller bearings are typically used in applications where high load-carrying capacity is needed.
- Thrust ball bearing – used in low thrust applications where there is little axial load. They are available in two designs: single direction and double direction.
- Cylindrical thrust roller bearing – give good carrying capacity.
- Tapered thrust roller bearing – most commonly used in automotive applications. They can support greater thrust loads than the ball type due to the larger contact area. They are designed to accommodate combined loads, i.e., simultaneously acting radial and axial loads.
- Spherical thrust roller bearing – Spherical roller thrust bearings offer the highest load rating density of all thrust bearings.
Four Thrust Bearings for Every Need
1. Oil-Embedded – used for applications with frequent starts and stops, the oil lubricates the bearing during startup
2. Dry-Running – operate with less friction and can work in high-temperature environments
3. Food-Grade – made of FDA listed materials for use in food applications
4. Corrosion-Resistant – high strength makes them suitable in marine and mining applications
Material Used in Thrust Bearings
The most common materials used to produce thrust bearings are stainless steel and ceramic. The cage is made of brass or steel, depending on the application.
Chapter 2 How to Select the Type of Bearing [Structures of Thrust Bearings]
When selecting the right bearing, it is essential the bearing fits the requirements for its use.
Meaning…
You must select the right bearing type based on the direction of the load.
| Categorization of Bearing Types | Rolling Element | Rolling Element |
|---|---|---|
| The direction in which force is mostly applied | Ball | Roller |
| Perpendicular to the shaft (radial load) | Radial ball bearing | Radial roller bearing |
| The same direction as the shaft (axial load) | Thrust ball bearing | Thrust roller bearing |
The force applied to a bearing is called the “load.” There are the radial and axial loads applied to a bearing. The force applied vertically to the shaft is called the radial load, and the force applied in the same direction (parallel) as the shaft is called the axial load.
Radial bearings support the force that is applied vertically to the shaft. Thrust bearings support a force applied in the same direction as the shaft.
An axial or thrust bearing uses side-by-side races. The race on the side into which the shaft is inserted is called the shaft race. The race inserted into the housing is called the housing race. [source]
Chapter 3 Bearing Applications in Different Industries
Benefits to Thrust Bearings
- They offer high reliability
- Provide high load capacity in harsh environments
- Simple mounting – the shaft and housing washers can be mounted separately
- Provide a wide assortment
- Availability
Roller thrust bearings have higher load carrying capacities than ball thrust bearings. The higher-speed applications require oil lubrication.
How does a thrust bearing work
There are various types of thrust bearings, each with its strength. The unique bearings deliver different performance and load capacities.
Thrust ball bearings are used in industries such as aerospace, chemical industry, and utilities. Thrust roller bearings are suitable for agriculture and other sectors that require high-load capacity.
Thrust bearings are also commonly used in automotive and marine applications. They are used in cars because the forward gears in modern car gearboxes use helical gears, which, while aiding in smoothness and noise reduction, cause axial forces that need to be dealt with. [source]
Thrust shafts are often used in the following industries:
Chapter 4 What Causes Thrust Bearing Failure and How to Avoid Them
When a bearing does fail, it is vital to determine the exact cause so adjustments can be made.
The three most common causes of thrust bearing failure are contaminants, misalignment, and overloading.
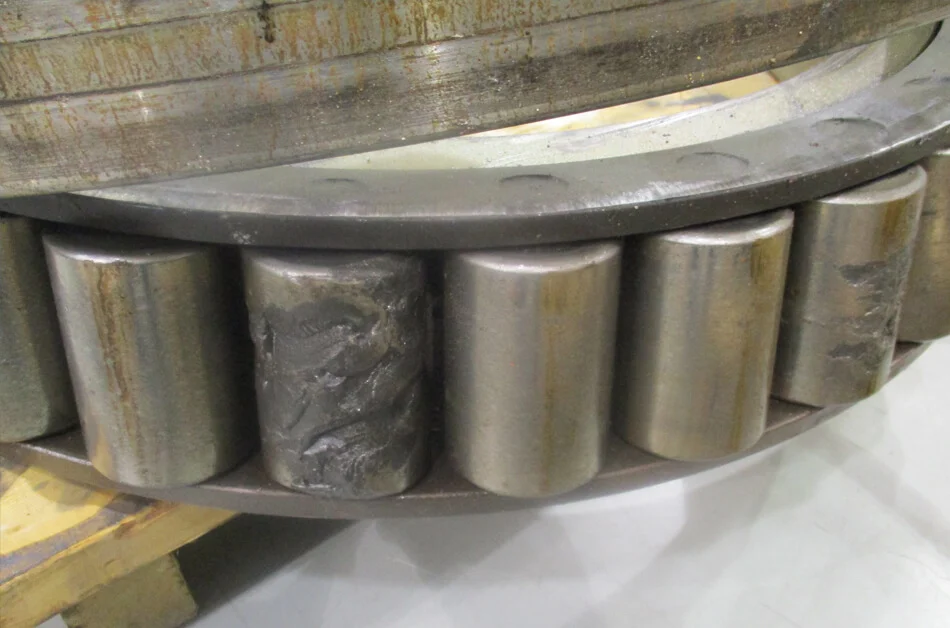

1. Contaminants
Contamination is one of the leading causes of bearing failure. Airborne dust, dirt, sand, and water are the most common ones you run into, but chemicals and corrosives can also damage bearings.
What to look for: Watch for denting of rolling elements and raceways that cause vibration.
How to Fix it: Filter the lubricant and clean work areas, tools, fixtures, and hands to reduce contamination risk.
2. Misalignment
Misalignments lead to excessive vibration and loads.
What to look for: According to Bearing Failure: Causes and Cures, the most commonly found causes of misalignment include: bent shafts, dirt or burrs on the shaft or housing shoulders, shaft threads that are not square with shaft seals, and locking nuts with faces that are not square to the thread axis.
To prevent misalignment, there are a few best practices you can keep in mind.
How to Fix it: Ensure you inspect shafts and housing regularly, use precision-grade locknuts, and shim the housings as needed.
3. Overloading
Putting too much load on a bearing is another common cause of failure.
What to look for: This may look like normal fatigue. You may see heaving rolling-element wear paths, evidence of overheating, and widespread fatigue areas.
How to Fix it: Reduce the load or consider a redesign using a bearing with greater capacity.
When a bearing fails, it negatively impacts your facility, your reputation, and your bottom line. Regular preventive measures can keep your bearings at peak performance for as long as possible, saving your business time and money.
You can take preventative measures to increase your bearing’s lifespan and prevent improper wear on them. Read more from BDS, “What Causes Bearing Failures and Preventative Measures.”
As a global leader in the bearing industry, TFL provides customized solutions to lead your industry. We find a solution to get the bearings you need and shorten your long lead time. Whether it is a bearing that is modified, manufactured, or repaired according to your specifications, we can help you.
Contact: Candice
Email: info@tflbearing.com
MP/Whatsapp: (86)15806631151
WeChat: 15806631151