Cylindrical Roller Bearings vs. Spherical Roller Bearings: 5 Key Differences & Guide
Introduction
Choosing between Cylindrical Roller Bearings (CRB) and Spherical Roller Bearings (SRB) is a critical decision that affects machine performance and maintenance intervals. While both are designed for heavy-duty industrial applications, they excel in opposite environments.
The main difference between cylindrical and spherical roller bearings lies in their ability to handle misalignment and axial loads. Cylindrical roller bearings are engineered for high speeds and stiffness under heavy radial loads. In contrast, spherical roller bearings are the go-to solution for applications involving shaft misalignment, shock loads, and heavy axial forces.
To help you make a quick decision, here is a snapshot comparison of their performance characteristics:
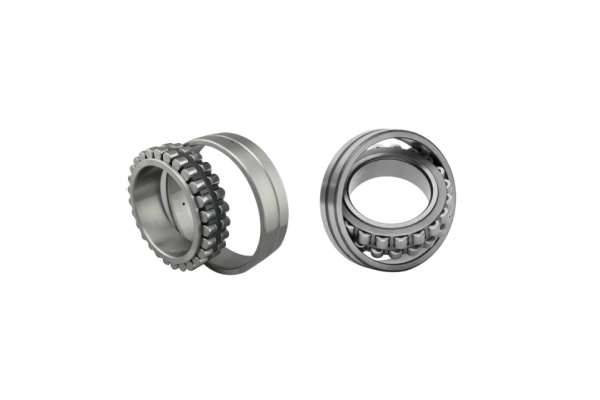

Quick Comparison: Cylindrical vs. Spherical
| Feature | Cylindrical Roller Bearing (CRB) | Spherical Roller Bearing (SRB) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | High Speed & Precision | Misalignment Handling & Heavy Load |
| Radial Load Capacity | Very High | Excellent (Heavy Duty) |
| Axial Load Capacity | Limited (Low to Moderate with ribs) | High (Supports two-way axial load) |
| Speed Capability | High (Low friction generation) | Moderate (Higher running friction) |
| Misalignment | Zero / Poor (Sensitive to tilt) | Excellent (Self-aligning up to 2°) |
| Mounting Difficulty | Easier (Separable rings) | Moderate (Non-separable) |
| Best Applications | Electric Motors, Gearboxes, High-speed Spindles | Vibrating Screens, Mining Crushers, Conveyors |
5 Key Differences Between Cylindrical and Spherical Roller Bearings
To choose the right component, you must understand the specific difference between cylindrical and spherical roller bearings in operation. Here are the 5 critical factors:
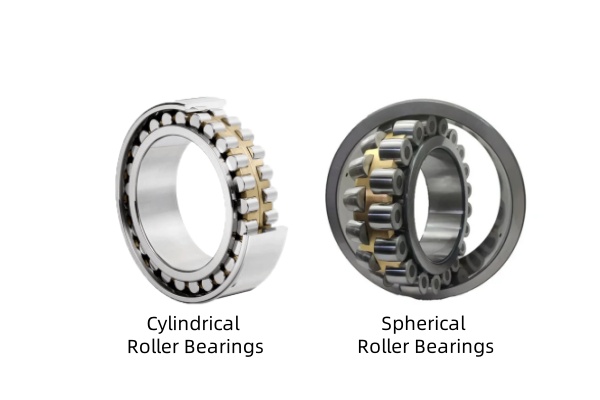
Structure and Contact Area
The primary structural difference lies in the contact patch. Cylindrical rollers have a linear contact area with the raceway, providing exceptional stiffness and rigidity. They typically consist of a separable inner or outer ring, which simplifies mounting.
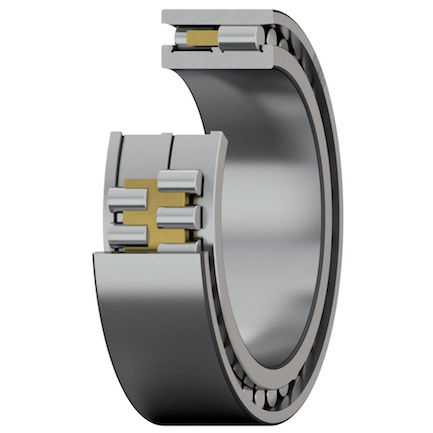

In contrast, spherical rollers are barrel-shaped and sit in a curved outer raceway. This design creates a point-to-oval contact, which offers flexibility but slightly less rigidity than cylindrical types.

Load Capacity and Direction
While both handle heavy loads, the direction of the load is the deciding factor.
-
Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Built for extremely high radial loads. However, standard designs handle only limited or no axial (thrust) loads.
-
Spherical Roller Bearings: Designed to support heavy radial loads plus significant axial loads in both directions. If your application involves combined loading, the spherical design is the winner.

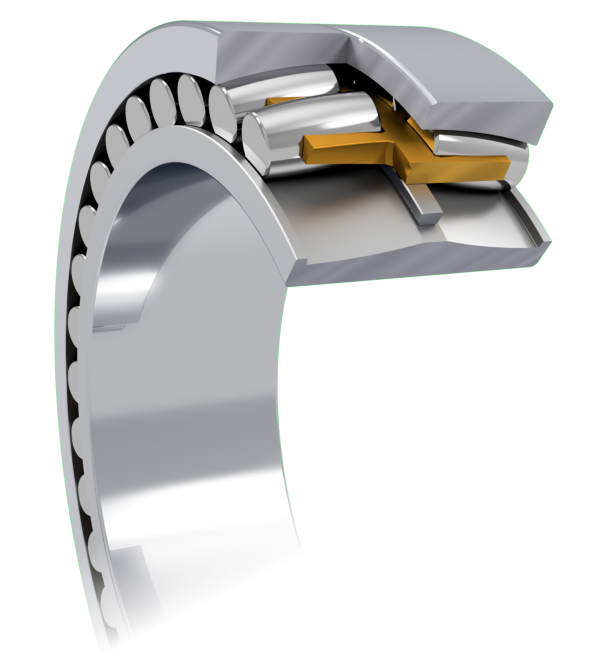
Misalignment Tolerance
Spherical roller bearings are self-aligning. They can accommodate angular misalignment (typically 0.5° to 2°) caused by shaft deflection or mounting errors without failing.
Cylindrical roller bearings are intolerant of misalignment. Even a slight tilt can cause edge stress concentration, leading to rapid bearing failure. They require precise alignment.
Speed and Friction
Cylindrical roller bearings generate significantly lower friction due to their line contact and precise guidance. This makes them ideal for high-speed applications.
Spherical roller bearings, due to their oscillating geometry, generate higher friction and heat. They are generally limited to low-to-moderate speeds compared to their cylindrical counterparts.
Mounting and Maintenance
Maintenance teams often prefer Cylindrical Roller Bearings because many designs (like N, NU types) are separable. You can mount the inner and outer rings independently, making installation and removal easier.
Spherical Roller Bearings are typically non-separable units. While they save time by forgiving misalignment errors during installation, replacing them on large shafts often requires tapered bores or hydraulic nuts.
Applications of Cylindrical and Spherical Roller Bearings
Choosing the wrong bearing for an application is the leading cause of premature equipment failure. Here is a breakdown of where each type excels based on their load and speed characteristics.
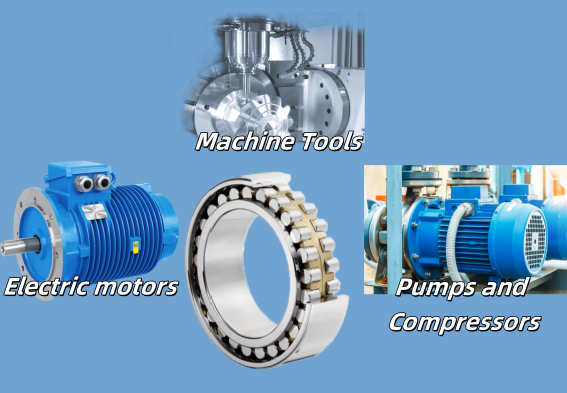
Cylindrical Roller Bearing Applications (Precision & Speed)
Because they offer high stiffness and low friction, cylindrical roller bearings are the standard choice for systems requiring precise shaft alignment and high rotational speeds. Common uses include:
- Machine Tools: The high rigidity of cylindrical rollers prevents shaft runout, ensuring precision in cutting and machining.
- Electric motors: Their low friction characteristics ensure quiet operation and energy efficiency at high speeds.
- Pumps and Compressors: Ideal for steady, high-speed fluid handling systems with stable loads.
-
Industrial Gearboxes: Used on the high-speed input shafts where heavy radial loads must be supported in a compact space.
Spherical Roller Bearing Applications (Heavy Duty & Misalignment)
Spherical roller bearings are the industry’s problem solvers. They are engineered for the harshest environments where dirt, vibration, and shaft deflection would destroy other bearings. Key applications include:
- Mining and Aggregate (Vibrating Screens): This is the ultimate test. SRBs can handle the extreme vibration and shock loads found in crushers and shakers.
-
Heavy Construction Equipment: Essential for off-road machinery where chassis twisting causes unavoidable shaft misalignment.
-
Steel and Paper Mills: Their ability to handle heat and heavy loads makes them perfect for continuous casting machines and paper rollers.
-
Wind Turbines: Used in the main shaft to accommodate variable wind loads and structural flexing.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Cylindrical and Spherical Roller Bearings
Deciding between these two bearing types often comes down to analyzing your specific operating environment. Don’t just look at the dimensions; consider the “health” of your machinery. Use this 4-point selection checklist to make the right call:
1. Is there Shaft Misalignment? (The #1 Factor)
Analyze your equipment structure. Is the shaft long and prone to bending? Is the mounting base uneven?
-
Choose Spherical Roller Bearings if there is any risk of misalignment (angular error > 0.05°). Their self-aligning nature will prevent edge loading and early failure.
-
Choose Cylindrical Roller Bearings only if the housing and shaft are perfectly aligned and rigid.
2. What is the Load Direction?
Check the forces acting on the shaft.
-
Choose Cylindrical if the load is 90% Radial (perpendicular to the shaft). They handle pure radial loads more efficiently.
-
Choose Spherical if you have Combined Loads (Radial + Axial). If there is significant thrust load pushing along the shaft, cylindrical bearings (standard types) will fail prematurely.
3. Operating Speed (RPM)
-
Choose Cylindrical for electric motors, fans, or spindles running at high speeds. Their low-friction design runs cooler.
-
Choose Spherical for heavy, slow-moving machinery like conveyors or crushers where speed is secondary to load capacity.
4. Installation and Maintenance
-
Choose Cylindrical if you need frequent mounting and dismounting. Types like N and NU have separable rings, making maintenance significantly faster.
-
Choose Spherical if you want a “fit and forget” solution for difficult environments, as they are more robust against mounting errors.
Summary: Selection Matrix
| Factor | Cylindrical Roller Bearings (Choose if...) | Spherical Roller Bearings (Choose if...) |
|---|---|---|
| Load Requirements | Application has Very High Radial Loads but minimal axial (thrust) force. | Application involves Heavy Combined Loads (Radial + Axial) or shock loads. |
| Alignment Needs | Shaft and housing are perfectly aligned (Rigid structure). | Shaft is prone to deflection, bending, or misalignment (Flexible structure). |
| Operating Speed | System requires High RPM with low noise and low heat generation. | System runs at Low to Moderate speeds; heat generation is less critical. |
| Environment | Controlled environments (Clean, stable temperatures). | Harsh environments (Mining, vibration, dirty conditions). |
| Maintenance | Frequent disassembly is required (Separable rings make it easier). | Fit and forget" reliability is needed in difficult-to-reach areas. |
Maintenance and Longevity
Inspection and Lubrication
While both bearings require clean lubrication, their maintenance demands differ. Cylindrical roller bearings are generally easier to inspect; types with separable rings allow for independent checking of raceways. Spherical roller bearings are more sensitive to lubrication quality because the sliding friction between the rollers and guide rings generates more heat.
Common Failure Modes
-
Cylindrical Roller Bearings: The most common killer is Edge Loading. Since they cannot handle misalignment, any shaft tilt causes stress concentration at the roller edges, leading to premature flaking.
-
Spherical Roller Bearings: Watch out for Overheating and Smearing. Because they have higher internal friction, running them above their rated speed reference will degrade the lubricant rapidly.
Both types’ lifespans can be significantly extended by using automatic lubricators and ensuring the correct internal clearance (C3, C4) is selected during installation.
Conclusion
The battle between Cylindrical vs. Spherical Roller Bearings isn’t about which is better, but which fits your “machinery health.”
-
Choose Cylindrical for Speed and Precision (Motors, Spindles).
-
Choose Spherical for Forgiveness and Heavy Loads (Mining, Conveyors).
Don’t let a bearing choice become a bottleneck. If you are still unsure about the load calculation or misalignment risks, contact TFL’s bearing specialists today. We can help you analyze your operating conditions to find the most cost-effective solution.
FAQs About Cylindrical and Spherical Roller Bearings
Can spherical roller bearings replace cylindrical roller bearings?
Yes, but with conditions. Spherical roller bearings can replace cylindrical ones if the application suffers from shaft misalignment or heavy shock loads that are causing the cylindrical bearings to fail. However, you must verify the operating speed. Since spherical bearings run hotter, they cannot replace cylindrical bearings in high-speed applications (like electric motors) without risking overheating.
How do I calculate the load capacity for cylindrical and spherical roller bearings?
You shouldn’t guess. Check the manufacturer’s catalog for two specific values: Dynamic Load Rating (C) for moving parts and Static Load Rating (Co) for stationary loads. Generally, for the same bore size, spherical roller bearings have a higher radial load rating than cylindrical types due to their robust design.
What are the key maintenance tips for extending bearing life?
Apart from regular greasing, focus on vibration analysis and temperature monitoring. An unexplained rise in temperature usually indicates over-lubrication or friction issues in spherical bearings, while increased vibration often signals misalignment damage in cylindrical bearings.
What materials are cylindrical and spherical roller bearings made of?
Standard industrial bearings are made from Through-Hardened Chrome Steel (SAE 52100) for durability. For extreme conditions, TFL also offers variants with Case-Carburized Steel for shock resistance or hybrid ceramic rollers for electrical insulation.
