Cylindrical Roller Bearings Maintenance: The Industrial Guide to Preventing Failure
Introduction
Cylindrical roller bearings are critical components in heavy-duty machinery, engineered to handle immense radial loads and high speeds. However, without a strict preventative maintenance strategy, even the highest-quality bearings can fail prematurely.
Industry data suggests that over 30% of bearing failures are caused by improper lubrication, while another significant portion stems from contamination and poor installation.
This guide moves beyond the basics. We will provide a technical checklist for maintaining cylindrical roller bearings, covering lubrication intervals, contamination control, and early failure detection to maximize equipment uptime and ROI.

Common Causes of Premature Failure
Before implementing a maintenance schedule, it is critical to understand why cylindrical roller bearings fail. According to industry studies, less than 10% of bearings reach their calculated fatigue life. The vast majority fail prematurely due to preventable external factors.
For cylindrical roller bearings specifically, which are designed for heavy radial loads, the primary failure modes differ from standard ball bearings.
Improper Lubrication (The #1 Culprit)
Lubrication issues account for nearly 36% of all premature bearing failures. In cylindrical roller bearings, the roller ends and flange contacts are subject to sliding friction. If the lubricant film strength is insufficient or if the wrong viscosity is used, metal-to-metal contact occurs, leading to rapid heat generation and scoring.
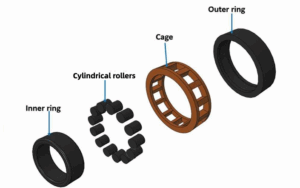
Misalignment
Unlike spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings have limited capacity to accommodate misalignment. Even a slight angular misalignment between the inner ring and outer ring (see diagram above) can cause edge loading. This leads to extreme stress concentrations at the roller ends, resulting in early fatigue spalling.
Contamination
Foreign particles—such as dust, metal chips, or moisture—act as abrasive agents. Once these contaminants enter the cage or adhere to the rollers, they grind against the raceways, destroying the precision geometry of the bearing.
Keep Cylindrical Roller Bearings Clean and Free of Dirt
Why Dirt Is A Problem for Cylindrical Roller Bearings

How to Keep Cylindrical Roller Bearings Clean
-
Use covers or seals to protect them from dirt.
-
Inspect them regularly. If you see dirt or grease buildup, clean it off right away.
-
Use a soft cloth or brush and a cleaning solution made for bearings. Avoid water—it’s not your friend here.
Lubricate Cylindrical Roller Bearings Regularly for Smooth Operation
Why Lubrication Matters for Cylindrical Roller Bearings

How to Pick the Right Lubricant for Cylindrical Roller Bearings
-
Check your machine’s manual for the right type of grease or oil.
-
Think about the environment—hot or dirty conditions may need special lubricants.
-
Proper lubrication is crucial for bearing longevity. For a comprehensive guide on bearing lubrication techniques and best practices, see our detailed article here.
How Often Should You Lubricate Cylindrical Roller Bearings?
Check Cylindrical Roller Bearings for Signs of Wear and Damage
What to Watch For
-
Cracks or rust.
-
Odd noises or vibrations when the machine is running.
-
Rough or jerky movement if you rotate them by hand.

What to Do If You Spot Damage
Avoid Overloading Your Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Why Overloading Happens

How to Avoid Overloading Cylindrical Roller Bearings
-
Don’t push your machines beyond their limits—check their load capacity.
-
Balance the load so the cylindrical roller bearings wear evenly.
Store Cylindrical Roller Bearings Properly When Not in Use
Why Storage Is Important for Cylindrical Roller Bearings
How to Store Cylindrical Roller Bearings Right
-
Keep bearings in a cool, dry place—away from moisture.
-
Use the original packaging to protect them from dust and scratches.
-
Don’t stack heavy things on top of the bearings.

